Bronfenbrenners Ecological Systems Theory | Microsystem |Mesosystem | Ecosystem| Macrosystem
What is Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model?
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory (EST) was developed to explain human development. The theory explained how the environment affects an individual’s development and psychology.
It is a framework for understanding the development of children and their contexts. It emphasizes that individuals are influenced by different contexts, including family, school, peer group, and neighborhood.
The theory was proposed in 1979 by Urie Bronfenbrenner to incorporate other theories into one comprehensive system with stages that can be applied across settings.
In the late 1960s, Urie Bronfenbrenner became interested in improving the quality of youth services. He became well known for saying, “what we now need to do is learn how to use what we already know about children and develop a scientific basis for applying this knowledge” (Weick, 1979).
To make significant contributions in child development, it was necessary to improve our understanding of how the various levels were connected together.
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory is a framework that highlights the interactions between multiple levels of an individual. It also establishes how these factors influence each other and cause complex developmental outcomes.
History Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
The Ecological Systems theory is a framework for understanding the effects of the environment on human behavior. It was developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, an American psychologist, and professor at Cornell University.
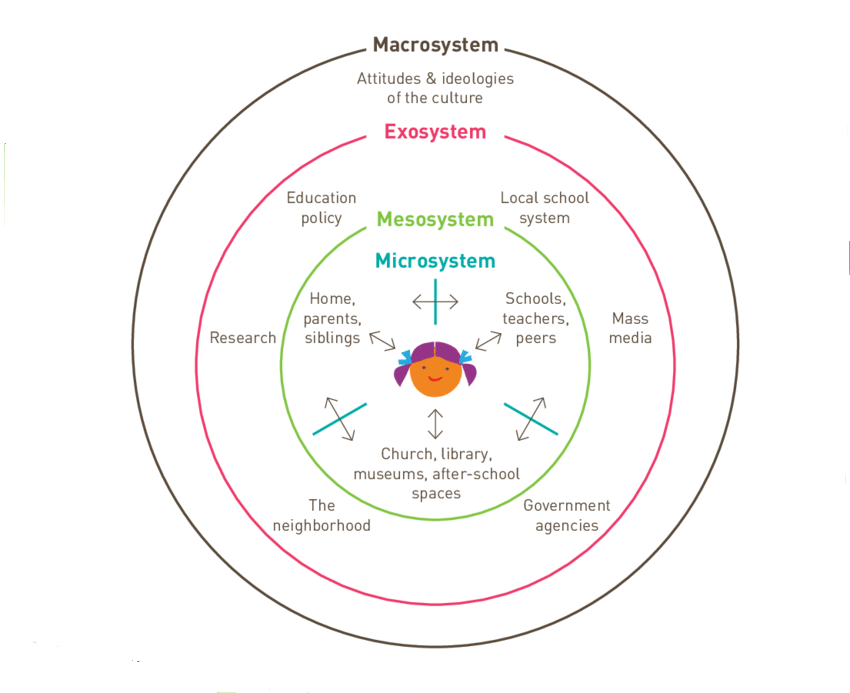
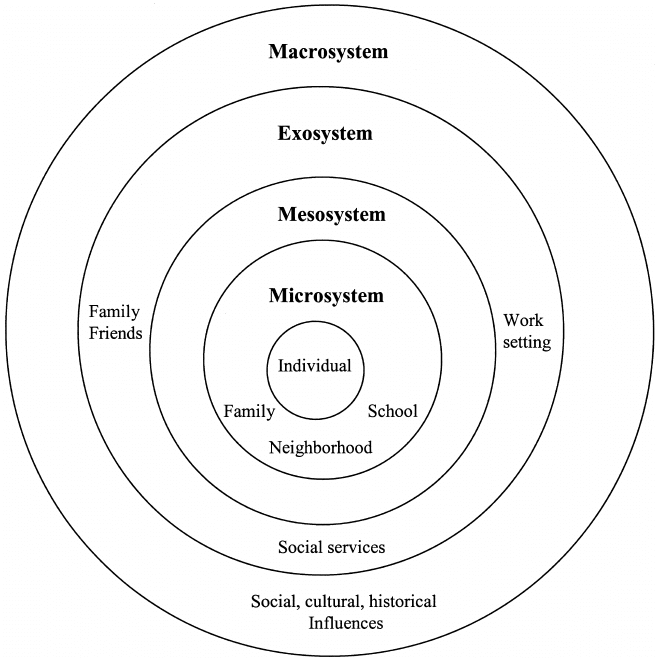
Bronfenbrenner published his first article in 1979, “The Ecology of Human Development,” and this article introduced his concept of four interacting systems: microsystem, mesosystem, ecosystem, and macrosystem.
These systems are nested within one another; they are not separate entities.
Bronfenbrenners Ecological Systems Theory
What is ecosystem
An ecosystem can be defined as a community of organisms and their physical environment interacting with each other in ways that sustain both themselves and the environment around them.
The theory suggests four distinct systems, which include;
- Microsystem
- Mesosystem.
- Exosystem.
- Macrosystem.
Microsystem refers to the family structure in which individual lives; while Meso-level depicts relationships among various groups with shared interests like schools or workplaces; Exo-level elements are those that influence individuals but not directly involved in their daily activities such as economic status; finally, Macro-level describes the physical settings where people live and work at large.
Urie Bronfenbrenner Ecological Theory of Development
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory (EST) is a human development model that stresses the importance of both biological and social-cultural factors to an individual’s growth. The theory, which has been frequently updated since its original conceptualization in 1979 by Urie Bronfenbrenner, is unique compared to other developmental theories due to its interdisciplinary approach.
Urie Bronfenbrenner Ecological Systems Theory Child Development
The Urie Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model is a framework for family ecology that focuses on the effects of the multiple aspects of the environment in which children are growing up.
Urie Bronfenbrenner was a pioneer in environmental psychology and is known for his work on ecologically oriented approaches to human development.
His ecological systems theory focuses on the importance of different levels impacting each other within an individual’s life path. He found that the social environment (e.g., family) had greater significance than others previously thought.
In other words, individuals do not exist separately from their environments; rather, they are part of multiple interconnected systems.
The Bronfenbrenner Theory is a human development model that looks at how biological, social, and environmental factors interact to shape human growth.
These ecological factors include culture, biology, and the child’s personality. This theory dictates that environmental interactions affect individuals throughout their life stages.
Children develop in an environment that is influenced by the interaction of three factors:
- The biological characteristics of their parents.
- The environmental characteristics of the family, including its culture and social relationships.
- Events outside themselves.
Each factor affects how children perceive themselves, where they fit in, and how they act.
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems theory has four systems that affect individuals: microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, and macrosystem.
These systems are interconnected dynamically through different interactions between people within them and their environments.”
Microsystem Bronfenbrenner Child Development
What is Microsystem?
Microsystem refers to the family structure in which an individual lives and is the second smallest unit of Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems. It is closest to the individual, and it contains all the people who are a part of one’s life.
The microsystem is the immediate environment of the individual, including their home and family. Every person has several microsystems– each with its own roles and rules.
Microsystem Bronfenbrenner Examples
Microsystem examples include:
- The family as a system with the child and parent in it.
- The school as a system with the teacher, students, and parents in it.
- Home and family
- School and work.
- Neighborhood and community.
- Workplace
Mesosystem Bronfenbrenner Child Development
What is Mesosystem?
A mesosystem is one of four interconnected levels of the environment. It is an area that contains more than two ecosystems and exists in a state of constant change as the systems around it do.
A mesosystem can be defined as “the set or complex of several interrelated ecosystems (or biomes) in close physical, chemical, etc. relationship with each other, but with differences from place to place” (Vitousek et al., 1987).
The word “meso-” comes from Greek and means “middle.”
The mesosystem connects individuals to other people in a larger system, such as friends or coworkers. The mesosystem is the environment that includes an individual and their immediate surroundings.
Mesosystem Examples
Some Mesoystem examples include:
- The school is a subsystem of society that interacts with the family system.
- A peer group is an example of an informal social organization that can be part of either the family or school subsystems.
- An individual’s work environment can also be considered as a mesosystem.
- Workplace, including workgroups and organizations that are not the individual’s employer.
- Community, including neighborhoods and religious institutions
Exosystem Bronfenbrenner Child Development
What is Exosystem?
The exosystem refers to all of the social environments outside of a person’s direct experience but still influences them (e.g., family, friends).
The exosystem is the environment that surrounds a person, which includes their home and community. The exosystem is the environment outside of a system, such as an organism’s habitat.
The exosystem is a system that influences another system but is not influenced by it.
Examples of Exosystem Bronfenbrenner
- An example of an exosystem would be a school or workplace.
- Another example of an exosystem would be where plants grow on your windowsill.
- Another example would be a school’s influence on students’ families.
- The exosystem includes all of the environmental factors that affect an individual’s life, such as climate change and pollution.
Macrosystem Child Development
What is Macrosystem?
The macrosystem refers to a larger system outside the individual’s direct experience. They include societal forces that affect people’s behavior and actions at large scales.
Ecosystem functions within a larger system called its macro system, including the biotic components such as plants and animals and abiotic components like rocks and minerals.
Macrosystem Example
- The macrosystem examples include things such as national culture or global economy.
- The laws and policies.
- Cultural norms.
Chronosystem Bronfenbrenner Child Development
What is Chronosystem?
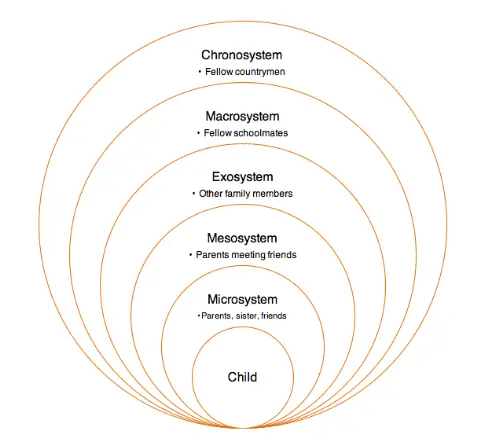
Chronosystem is the fifth and final category of the ecological system Theory of Bronfenbrenner. Chronosystem refers to forms of all the experiences that a person has had over his or her lifetime.
Chronosystems are the time-based systems of an individual’s life, such as a day or week. The chronosystem regulates biological rhythms and circadian cycles that govern sleep, appetite, temperature regulation, and hormone release.
Chronosystems also regulate social rhythms like work schedules and school hours.
Chronosystem Example/Examples of Chronosystems
Examples of chronosystem including environmental events, major life changes, and historical events.
Bronfenbrenner Theory in The Classroom/Examples of Bronfenbrenner’s Theory in The Classroom.
Bronfenbrenner’s theory in practice focuses on children’s social, emotional, and cognitive development as they interact with their environment.
Bronfenbrenner’s theory of ecological systems has been used in many different fields for different reasons. It suggests that a child’s development can be affected by the number and type of people in their environment, including school.
In education, it can be useful because the classroom is an ecosystem that includes more than just teachers and students.
The school’s context, state laws, local policies, and even individual interests affect students’ development. It, therefore, shows that factors outside of the student-teacher relationship play a role in learning.
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Model can help understand the student’s learning environments and establish quality learning environments.
The teacher can do this by recognizing he or she is a part of the student’s microsystem. As a part of this system, they need to be a positive role model for the students to look up to.
An example could be following through on all commitments and listening to their students. This shows how students should act towards one another, therefore helping with the interactions with the mesosystem.
With this interaction, the teacher can better understand each student’s home life to take a closer environment. This can also be done by giving the students projects or homework that can be done at home in their parents/guardians’ presence.
The interaction at a program like this can strengthen the mesosystem and help the educator understand the students’ learning environment by interacting with their parents.
Application of Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model Example
In recent studies, the Ecological Systems Theory has been used to understand how stress is transmitted across a person’s life span. These studies have found evidence that one’s effects can be passed on to their children.
For example, if an individual experienced exposure to war as a child, they are likely to develop Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) when they reach adulthood.
Besides, some people believe that Ecological Systems Theory provides insight into why certain individuals experience chronic health problems during their lifetimes, such as depression.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ecological Systems Theory Model.
Advantages of ecological systems
- Advantages of ecological systems theory are that it can be used as a predictive tool, it offers an alternative view on how humans interact with their environment.
- Ecological systems theory is a theoretical framework for understanding the organization of living and non-living components in an ecosystem. Ecological systems theory is a holistic approach to understanding the natural world.
- The advantage is that this system takes into account all factors that are important for an ecosystem’s health, including humans.
- The ecological perspective has been applied in many fields. The theory has found wide application in many fields, including psychology and sociology, environmental science, earth sciences, ecology, biogeography, epidemiology, and economics.
Disadvantages of ecological systems
- Disadvantages of ecological systems theory include its complexity and difficulty for people to understand it.
- Another disadvantage of ecological systems are is that it can be difficult to measure human activities’ impact on ecosystems because they are large.