The Business Model Canvas for Startups | Business Model Canvas Example Skype
Business Model CanvasMeaning
Business Model Canvas is strategic management and entrepreneurial tool for developing new and documenting existing business models. It is a visual chart that allows you to describe the design, invent, and improve your business model.
It is a strategic planning tool that can be used to illustrate and make sense of these things about a company. It’s often used for startups, but it can also work well for established companies looking to rethink their strategy.
The business model canvas is made up of nine boxes, which show you the different levers of a company and how they are organized to address markets and customers.
The canvass contains nine building blocks, including the following:
- Customer segment
- Value proposition
- Channels
- Customer relationships,
- Revenue streams,
- Resource
- Activities,
- Partnerships
- Cost structure.
If you structure these 9 block segments in this formation, you will get the answer to all of your fundamental questions about any business idea.
This business canvas is for any idea, newer, existing.
Business Model Vs. Business Plans
The Business Canvas model has four advantages over the traditional business plan.
Focus.
Business Canvas is designed to guide you thinking through each of the nine building blocks for devising a business model business.
Canvas focuses on the strategic elements that matter most and have the greatest impact on driving growth.
It forces you to think of your business more systematically and formally.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Speed.
The business model is nine boxes into a single piece of paper, so you have to be consistent.
Startups never create a classic business plan in the early stage unless required by your bank or investor.
Changeable.
In the early stage of a startup, it is imperative to change things in your model easily. In the standard business plan, each small change will provide a lot of additional work.
The best way is to print a business canvas into big paper sheets or draw on a whiteboard and stick posted notes.
When you stick post-it notes on it, you can easily change how you figure out your business model.
It is a standard form that is understandable for everyone.
You can easily share, get feedback from your partner or investor, and update building a funny business model.
Business Model Canvas Example Skype
When you are using business models for your idea, there is no standard path from which building blocks you should start. If you are an entrepreneur, then you have extensive knowledge of the market.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
If you know the market segment, you should start with the customer segment; then, you continue with the value proposition.
But if you are an entrepreneur with the product idea, but you are not sure who your customer is, start with the value proposition.
Business Model Canvas Value Proposition
We will start with the Value Proposition, but remember, you can also start from customer segments.
The value proposition is the first box that we fill in. Its response to the following questions;
- This is about what problem do you solve with your product?
- What value do you deliver to the customer or which customer needs?
- Are they satisfied?
Business Model Canvas Value Proposition Example
Let’s take Skype as an example.
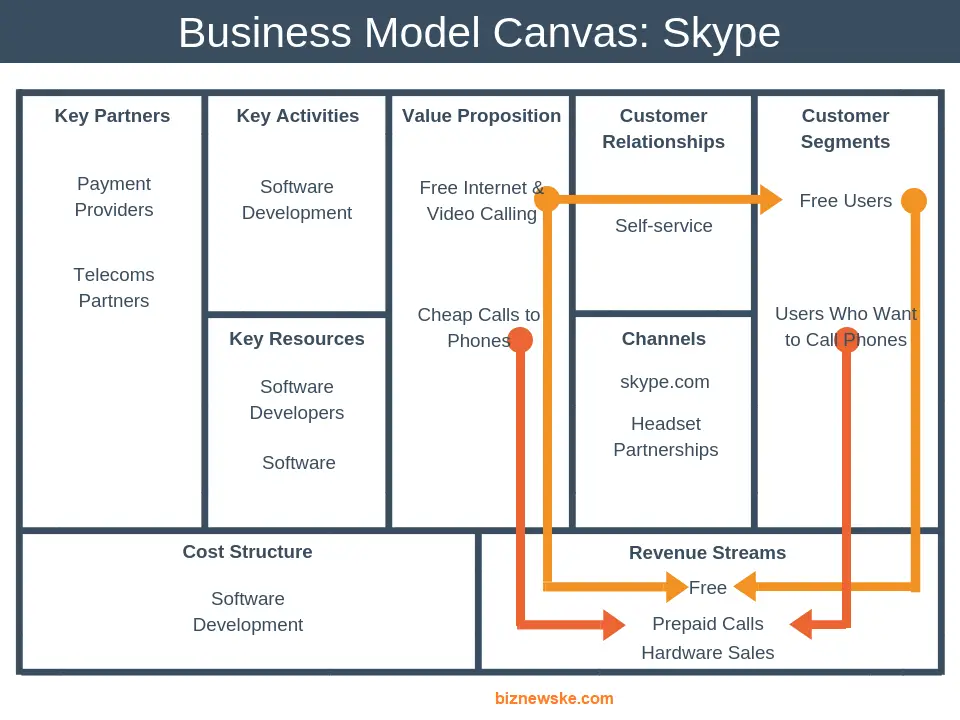
The value proposition for Skype is free Internet voice and video calls and low-cost calls to landing in mobile numbers.
Think about what problem you solve and fill in this field
Business Model Canvas Customer Segment
This is about for whom you are creating value?
Who is your product for, and who are your most important customers?
The purpose here in this box is to look deeper within the general market to locate customers with more specific needs for your product.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
You can fill this block info such as my target audience, our kindergarten teachers from 30 to 40 years old in New York.
Business Model Canvas Customer Segment Example
If we take Skype as an example.
The customer segment is people globally who hold meetings or call their families and friends and companies that want to make cheap international calls.
Business Model Canvas Channels
Which channels do your customer segments want to be reached? Remember, Channels doesn’t mean only. How do we deliver a value proposition to customers?
But also, how do we raise awareness about our product and service?
And how do you provide post-sales customer support?
Business Model Canvas Channels Example
If we take Skype as an example?
Channels that Skype uses to connect value proposition and customer segment are desktop application, mobile application, and website.
If we take the Apple iPad as an example, the channel that Apple uses for this product, our retail stores, Apple stores, and website
Business Model Canvas Customer Relationships
The next field is customer relationships, the types of relationships a company establishes with specific customer segments.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
This is about how do you get to keep and grow your customer base?
Business Model Canvas Customer Relationships Example
If we take the same example for Skype in this block, we will write down personal and self-service Skype software, download Skype subscriptions, etc.
Business Model Canvas Revenue Stream
It is about how do you generate cash from each customer segment. For what value are your customers willing to pay?
It is also about how they are currently paying and how would they prefer to pay?
It can be usage fees, asset sales, licensing, and so on.
Business Model Canvas Revenue Stream Example
Revenue streams for Skype are basic service and fee credit and subscriptions and Skype hardware.
Business Model Canvas Key Activities
What activities does a company engage in that allow it to execute its strategy and establish a market presence?
It is not about what you do. It is about the most important things a company must do to make its business model work.
Business Model Canvas Key Activities Example
For example, the key activities of Skype are software development and complaint management.
Business Model Canvas Key Resource
It is about the infrastructure and resources you need to deliver what you have promised? Or what is the key resource that you need to perform the key activities? This can be the equipment for humans’ licenses, financial requirements, and so on.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Business Model Canvas Key Resources Examples
Skype Key Resource is our software developer’s software and Skype brand itself.
Business Model Canvas Key Partners
Who do you need to make this work?
How does each partner help the business, or what strategic partnerships does a company form to increase its scalability and efficiency?
It can be suppliers, developers, distributors, inventors, collaborators, affiliates, and so on.
Business Model Canvas Key Partners Examples
In the Skype example, the key partners are payment providers, telecom companies, and distribution partners.
All of these key activities, key partners, and key resources are cost money, and all of these costs need to be written down in the cost structure block.
Here, you have to write down the most expensive key activities and key resource is all fixed and variable costs.
It is not about the ideas. It is about making ideas happen. So, grab your pen and start to work on your idea.
Business Model Canvas vs. Lean Canvas
The Business Model Canvas focuses on a company’s value proposition, customer segments, key activities, revenue streams, and distribution channels to deliver that value proposition to customers to create a sustainable competitive advantage for the organization over time. It also includes an assessment of how those elements might change over time and their potential impact on one another and on other aspects of the business model canvas, such as cost structure or pricing strategy.
The Lean Canvas is designed to help entrepreneurs rapidly test their startup ideas by identifying critical assumptions about what they are building (product/service), who they are building it for (customer), why people will want it (value), how much people will pay for it (price), where they can reach these customers with this product/service (distribution).
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Business model canvas is a strategic planning tool that helps entrepreneurs develop and test new business ideas. Lean Canvas is a lean startup’s go-to product development framework that allows them to quickly validate their idea before they start building the full product.
The Lean Canvas focuses on identifying customer segments and their needs and how you will provide a solution to meet those needs. In contrast, the Business Model canvas is focused on understanding your company’s value proposition, including key activities that generate revenue and deliver an experience for customers.
The Business Model Canvas focuses on the big picture of what needs to be done, while Lean Canvas provides more detail about how it should be done.
The two frameworks are similar in how they both use an 8-step process to help you create your plan. Still, there are some key differences between the two: Business model canvas focuses on what your customers want and need. In contrast, Lean Canvas focuses on what your potential customers want and need.