Judee Burgoon Expectancy Violation Theory
History of Expectancy violations theory
The expectancy violation theory was developed by Judee Burgoon, a theorist communications professor at the University of Arizona, in 1978.
Expectancy violations theory was originally derived from the theory of nonverbal violation expectancy violation. Judee Burgoon soon dropped the non-verbal term from the theory title because she felt as though the theory went beyond just nonverbal communication.
Before introducing Expectancy violations theory, an anthropologist from the Illinois Institute of Technology, Edward Hall, pitched the idea of Proxemics in 1960, where he studied individuals’ use of personal space.
According to Judee Burgoon, each culture has different expectancy boundaries and structures that are expected with personal space.
Expectancy is what an individual predicts, what will happen during interaction rather than what they desire.
What is Expectancy Violation Theory?
Expectancy violations theory can be defined as a theory that attempts to explain the influence of community nonverbal communication on people’s behaviors.
Expectancy violations theory tries to explain the consequences of non-verbal communication on behavior.
Expectancy violations theory, which is also referred to as EVT, defines personal space as an invisible element and interpersonal communication, which basically means we all have an expectation on nonverbal behavior with other people.
But if someone violates your expectations, it could make you uncomfortable or create a positive or negative reaction, and then it’s called an expectancy violation.
This is when an individual has a preferred distance surrounding others. This distance or space is also dependent on the cultural norms and personal preferences of a person. This is not an interpretive theory; instead, it’s an objective meta-theory.
Personal Space Proxemics & Personal Space Violation
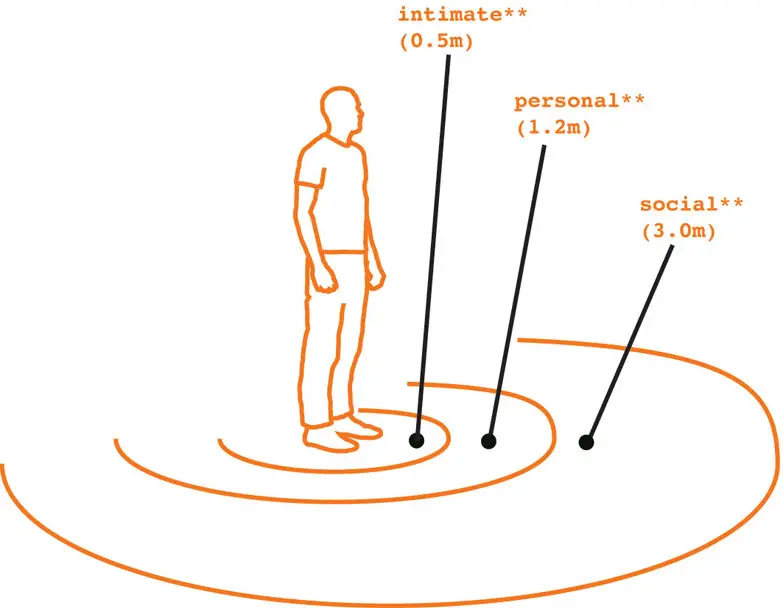
Personal Space Proxemics is defined as a study of a person’s use of space. Edward Hall claimed there were four proximate levels intimate, personal, social, and public.
One of the most important things is personal space. The following are the 4 different personal space levels;
- Intimate space
- Personal space
- Social space
- Public space
Personal Space Violation Example
Expectancy violations theory states that each person has an expectation of personal and conversational space. As humans, we have desires for close proximity, but we also desire space and distance.
What is Considered Personal Space?
Intimate Space
Intimate spaces between zero and 18 inches. This space is our most valuable and most protected space, and we only share with those who we wish to be intimate with, like a partner or spouse.

Personal Space
Personal space is a space between 18 inches and 4 feet and something that you would usually share with your friends and your family, or maybe even a sales clerk at a store.
Social Space
Social space is a space between 4 – 12 feet is basically like a classroom or a speech or a concert.
Public spaces
Public spaces are a space beyond 12 feet. Party gathering is a public space.
What Does Expectancy Violation Theory Entail
Expectancy Violation Theory has three core concepts, namely;
- Expectancy
- Communicator reward valence
- Violation Valence,
Expectancy
There are two types of expectancy, namely; Predictive expectancy and prescriptive expectancy.
Predictive expectancy
Predictive expectancy focuses on communication and interaction happening within context.
Prescriptive expectancy.
Prescriptive expectancy focuses on the behaviors appropriate to the environment,
Expectancy itself is affected by three factors. The three factors are;
Communicator characteristics: means what the communicator individually brings to the interaction.
Relational characteristics: so that means the dynamic of the communicator and the person being communicated with
The context: it is the environment of the situation.
Communicator Reward Valence
The communicator reward violence basically focuses on the encounter leave the communicated with what they wanted or needed, and their positive and negative attributes brought to the encounter.
It focuses on the potential to reward or punish the communicatee in the future. The reward basically focuses on the person’s ability to provide you with what you wanted or needed out of the interaction.
Violation Valence
Violence Valence is a perceived positive or negative value assigned to the breach of expectation. In other words, it is the positive and negative interpretation of the violator’s behavior.
Violation valence is also a key component in this theory. According to Judee Burgoon, the violation valence refers to the positive or negative value we place on a specific unexpected behavior, regardless of who does it.
This eventually leads to the communication reward valence, which is the reaction individual has to the unexpected behavior, whether positive or negative.
EVT also assumes that we already have attitudes about expected nonverbal behaviors. When we evaluate and interpret these behaviors thin, that’s when we accept or disapprove of that violation.
Expectancy Violation Theory Experiment
Expectancy Violation Theory Example
Danette Johnson and Nicole Lewis wrote a journal called Perceptions of Swearing in the work setting. An Expectancy Violations Theory Perspective, in which the study was conducted to understand people’s reactions to swearing messages in the workplace.
The study was conducted because there’s not enough research on how people react to swearing messages in a formal environment.
They used the expectancy violation theory to analyze whether someone has a positive or negative expectancy violation.
And I think we’ve all experienced or worked at one point where we, or how we can react to swearing in a formal environment that is why we call this journal.
This study found that people have an unexpected reaction to swearing messages in any sort of formal gathering.
This could be at the workplace or in social gatherings. Hearers people who heard swearing, we’re much more likely to react with more aggressive swearing messages like f-u-ck off or compared … Oh shit or That sucks.
The study concluded that hearers were simply surprised that the swearing expressions and created evaluations of the speakers, which is an expectancy violation.
EVT is in every social interaction.
When we’re with friends, family, at work, or with a partner for each, we have certain expectations of nonverbal behavior.
EVT simply helps us understand people’s desires, space, and reactions.
Can you think of a time when your expectations were violated? What was your reaction?
Expectancy Violation Theory Examples in Movies
Limitations /Criticisms of Judee Burgoon Expectancy Violation Theory






