Kurt Lewin Force Field Analysis Model | Driving and Restraining Forces of Change
What is a Kurt Lewin Force Field Analysis?
The force field analysis is a useful technique for analyzing pressure factors for and against change and aids in deciding a plan or course of action.
In effect, it is a specialized method of weighing pros and cons. By carrying out analysis, you can plan to strengthen the factors supporting a decision, a plan, or course of action and reduce the impact of opposition to it.
The Force field analysis was first developed in 1951 by Kurt Lewin, a German-born psychologist and one of the modern pioneers of social, organizational applied psychology.
Kurt Lewin was one of the first researchers to study group dynamics and organizational development.
Lewin began his work in pre-World War two Germany and worked with a psychologist of the Gestalt school. When Hitler came to power in 1933, Lewin worked at the London Tava Stock Institute and then later immigrated to America.
In the USA, Lewin worked at the University of Iowa, Cornell University, and MIT, where he would become director of the Center for Group Dynamics.
While at MIT, Lewin set up a workshop defined in an effective way to combat religious and racial prejudices, which laid the foundations for what is now known a sensitivity training
In 1947 this led to Lewin’s establishment of the National Training Laboratories at Bethel, Maine, shortly before his death.
Driving Forces and Restraining Forces of Change
Borrowing a concept from physics called quasi-stationary equilibrium, Lewin noted that life’s perceived status quo is just that, a perception.
Lewin viewed organizations as systems in which the present situation was not a static pattern but a dynamic balance of forces working in opposite directions.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
These two opposing forces are;
- Driving forces; Those factors seeking to promote change.
- Restraining forces; Those factors attempting to maintain the status quo.
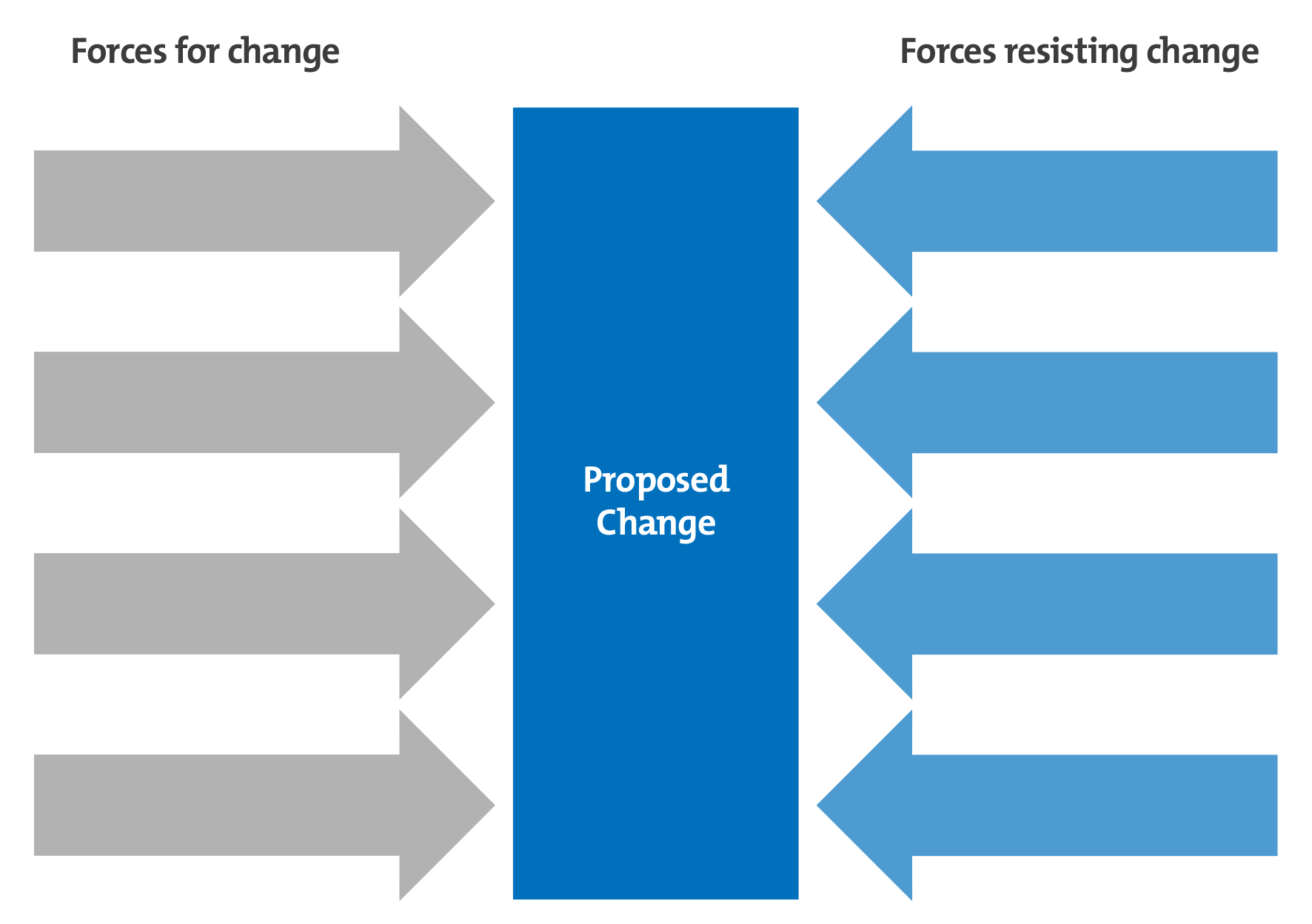
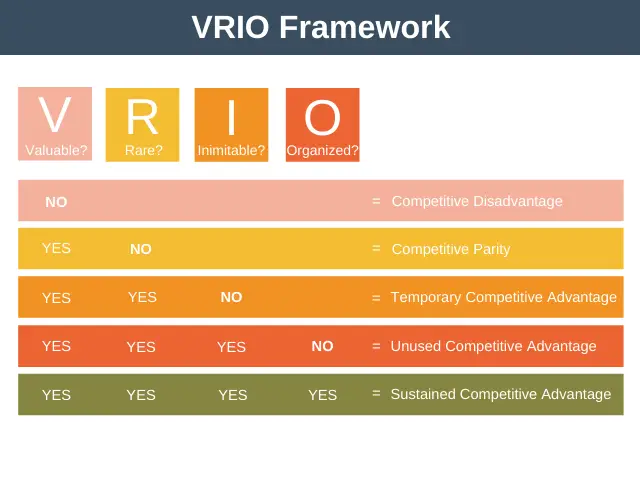
Kurt Lewin Force Field Analysis Template
Driving Forces For Change
Driving forces represent those forces that encourage change in some way.
Examples of Driving Forces For Change
For example, if an organization was adopting a new inventory management system, supervisor encouragement, monetary incentives, and even training could be considered driving forces.
Restraining Forces For Change
The second force at work is restraining forces. Restraining forces represent those forces that helped maintain the status quo and make the implementation of change much more difficult.
Restraining Forces Examples
For example, worker habits, hostility towards management, or even past experiences conservative forces that prevent, or at least lessen, the likelihood of the new system being adopted.
For any change to occur, the driving forces must exceed the restraining forces, thus shifting the equilibrium.
These organizational forces or factors can be;
- Culture
- People
- Organizational Structure
- Habits
- Customers
- Policies
- Procedures
- Behaviors
- Attitudes
The force field analysis is a method for listing, discussing, and evaluating the various forces for and against the proposed change.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
When a changes plan to force field analysis helps you look at the big picture by analyzing all of the forces impacting the change in weighing the pros and cons.
You can then develop strategies to reduce the impact of opposing restraining forces and strengthen the supporting driving forces.
Using force field analysis
Using this tool is a two-step process, namely;
- A force field analysis is conducted, and then the intensity of a force or set of forces is either increased or decreased. Change could be fostered by adding to or increasing the intensity of the driving forces.
- The change could be fostered by diminishing the opposing or restraining forces.
Lewins Change Theory proposed that the better of these two choices is to reduce the intensity of the restraining forces. This is because by adding forces or increasing the intensity on the driving side, a simultaneous increase would occur on the restraining side and the system’s overall tension.
Whether it’s a person, a group or an organization would intensify, the equilibrium would stay intact, and the status quo would persevere.
This idea he borrowed from the physical sciences, Isaac Newton’s law of action and reaction. It states in his third law of motion that there’s an equal and opposite reaction to every action.
The better choice then, according to Lewin, is to reduce the restraining forces. So if you want change to happen in the system, don’t try to force it into reducing the power and influence of those factors that resisted it from happening.
How to use Kurt Lewin Force Field Analysis Tool
Here are the first steps on how do you use the force field analysis template tool?
- On the template, described your plan or proposal for change in the middle.
- List all the forces for change in the Left column and all the forces against change in the right column.
- Assign a score to each force, with one being the weakest and five the strongest.
For example, imagine that you are a manager deciding whether to install new manufacturing equipment in your factory. You might draw up a force field analysis like the one and figure one.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Once you have carried out an analysis, you can decide whether your project is viable in the example in figure one, you might initially question whether it is worth going ahead with the plan.
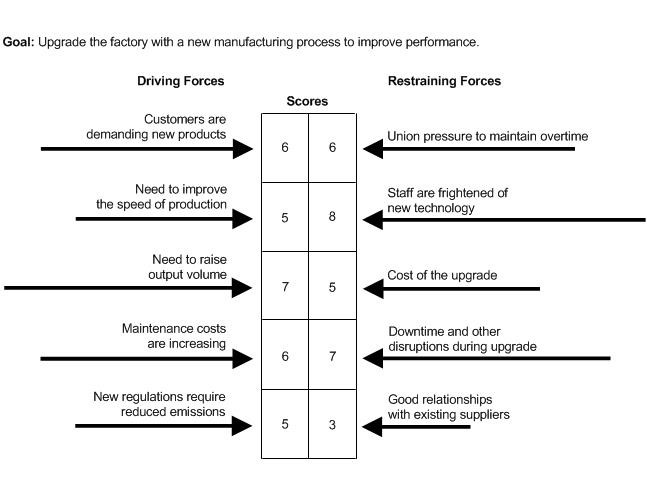
When you’ve already decided to carry out a project, the force field analysis can help you to work out how to improve its probability of success. Here you have two choices.
- To reduce the strength of the forces opposing a project, the restraining forces, or
- To increase the forces pushing a project, the driving forces.
As Lewin indicated, often the most elegant solution is the first, because just trying to force change through may cause its own problems. People could be uncooperative if changes are forced on them, going back to the example in figure one.
If you had to implement the project to install new machinery, the force field analysis might suggest a number of changes to the initial plan.
For example, by the training staff you could;
- You could eliminate some of the fear of technology, or
- You might show staff I’ll change is necessary for business survival.
- You could show staff how new machines would introduce a variety and interest to their jobs.
- You could raise wages to reflect new productivity.
- You could install slightly different machines with filters to eliminate pollution.
These changes could swing the balance from against the plan to being in favor of the plan.
Kurt Lewin Force Field Analysis Example
Example of Kurt Lewin Force Field Analysis application with some steps that management can take to increase the adoption rate to change.
A few days ago, Comcast announced and offered a by competing cable provider, Time Warner Cable, for $46 billion in stock. Let’s use it as an example with Force Field Analysis.
With the force field analysis, the first step is to outline the driving and restraining forces that are likely present in this scenario. This is unlikely to be an exhaustive list, but at least you’ll get a feel for how to conduct the analysis.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Driving forces may include;
- The enthusiasm and commitment of top management,
- The approval of the board of directors
- The support of the investment community.
These forces are considered driving forces because they encourage the change and the departure from the current equilibrium state.
But are they enough to move the equilibrium while they may, in fact, not be working against those driving forces could include?
- Employees who are concerned about layoffs
- Customers who are fearful of paying higher prices is cable options decrease.
- Establishment of new operating structure procedures that would need to change.
- In addition to these changes, the U. S government can always file suit and attempt to block the acquisition undergrounds to harms competition and subsequently consumers.
Now each of these forces doesn’t affect the situation the same, but all play some part in the current situation. Now that we’ve conducted a brief analysis of the present situation, we need to develop a change strategy.
The first question that we should ask is
Do the driving forces far outweigh the restraining forces?
If so, management will need to do very little to see the adoption of the change in our situation. This is unlikely given the nature of our restraining forces.
The second question we should ask is,
Are the restraining forces much stronger than the driving forces?
If the answer is yes, we have a couple of options.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
- We could do nothing. We realize that attempting to change the status quo would be far too difficult and give up altogether.
- The second option is that we can pursue the change effort by maintaining those driving forces while attempting to minimize the impact of those restraining forces, and
- The last possible situation occurs when the driving and restraining forces are similar in size. In this case, management can push the driving forces while slowly attempting to lessen the restraining forces.
Regardless of which option we choose, Let’s look at how we can increase those driving forces and decrease the restraining forces.
In our example, one of the first things that likely needs to be done is:
- To educate and communicate with our workforce.
They probably have many concerns, and rightfully so, educating them about the acquisition and what the new company would look like.
We can slowly start to chip away at those restraining forces, making change much more likely.
- To educate consumers and government officials.
It would also be important to educate consumers and government officials and inform them of how the company would operate post-acquisition and the potential impact on prices.
- Allow employees to participate in the change process actively.
The next action that we can take is to allow employees to participate in the change process actively.
Research shows that people are far more willing to go along with the course of action if they’ve been allowed to voice their opinion, even if the decided course of action is against what they proposed.
So, by involving employees in the process and allowing them to make decisions on how jobs will be performed. This may lessen some of the restraining forces at work.
- Providing managerial support of training and added incentives
Providing managerial support in the form of training, added incentives, and other actions can also decrease restraining forces and make the possibility of acquisition more of a reality.
Advantages & Disadvantages /Criticisms of Lewin Force Field Analyses
Advantages of Lewin Force Field Analyses
- One of Lewin’s force field analysis’s key advantages is that it presents a visual summary of all the various forces and factors opposing and supporting a particular change idea based on the information collected about a potential change decision consolidated into a single template.
- By using Lewin’s force field analysis techniques, organizations can better implement change and increase their chances of success.
Disadvantages /Criticisms of Lewin Force Field Analyses
- Force field analysis requires all stakeholders’ full participation to provide the accurate information and opinion required for an effective analysis. This can be criticism as full participation seems impossible in many organizations, resulting in a field analysis that doesn’t provide a realistic picture of the two forces.
- Another criticism is that the analysis may not result in a consensus among the teams/ group. In fact, a force field analysis may actually lead to division in the group between those who support the decision and those who oppose it.
- One of the key things to keep in mind when using force field analysis is that the analysis is dependent on the experience, knowledge, and skill level of the manager or group conducting the analysis. It can also lead to a force field analysis that is biased and with unrealistic assumptions.
- Another criticism of the force field analysis is that It usually focuses on the subjectivity of attributing scores to the restraining forces or driving forces.
- Some writers have also suggested that the model applies only within limited settings and that there are situations outside of these settings in which Lewin’s theory may be less applicable.