Littoral Zone Animals | Littoral zone Ecosystem | Littoral zone Ecosystem
Littoral zone
The littoral zone is a transition area between the ocean and the land. This area is also referred to as the shoreline. Bodies of water such as estuaries and bays are usually a type of littoral zone. The littoral zone is home to many marine life, such as seaweed, kelp, and clams. The littoral zone is an important part of the ecosystem and can be vital to the health of the environment.
Littoral zone is the name given to a part of the coastline that is affected by the meeting or mixing of saltwater from the ocean and freshwater from rivers or streams.
The zone can be divided into sub-regions, including submerged shore, wet shore, and dry shore. The main factors determining what type of zone are found in an area are salinity, tidal range, and sediment supply.
The littoral zone is located at the coastal margins of many different continents in the world. In addition to being found in the Pacific Ocean, it is also found in the Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, and various seas around South America, Africa, and Europe.
The littoral zone is found at the margins of many different continents around the world. It can be found in most oceans and seas.
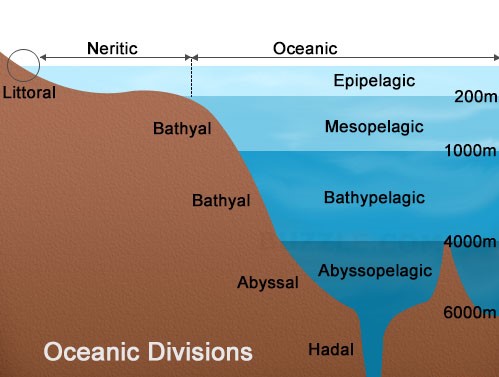
Littoral zone Ecosystem
Littoral zones have been studied extensively for decades by scientists and environmentalists. The area occurs naturally and can be both a hazard and a valuable habitat for wildlife. There are many different types of littoral zone habitats, including mangroves, salt marshes, mudflats, coral reefs, seagrass beds, etc.
From an ecological point of view, the littoral zone is a highly productive area. The ecosystem contains an abundance of plants and animals. The food web also contains a significant number of organisms, including commercially important fish species.
What’s more, over 90% of all marine fish species live in the littoral zone, and 50% are endemic to this area of the world.
Littoral Zone Animals
The zone is also the home to thousands of fish species, with more than 40% of the marine species being found in the littoral zone. The zone also acts as a nursery ground for several marine life species and can be a sanctuary for many fish and birds.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The coast is important for sustaining the ecosystems in many coastal areas. This is because it provides a habitat for a great diversity of species, which are found in many parts of the world. Besides, many economically important animals have their homes within this zone.
For example, about 60% of all cetacean species live primarily in littoral zones. They include whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Other animals found in the littoral zone include mollusks, crabs and shrimp, fish such as bass, snappers, and other crustaceans, starfish, sea urchins, and many invertebrates.
The littoral zone is also a key part of the world’s food web. The area provides a habitat for animals such as crabs, shrimp, snails, and oysters. These, in turn, are eaten by fish and birds, which humans in turn eat. In addition to this, seagrass meadows provide vital habitats for many fish species.
The littoral zone is home to many other economically important animals, including sea mammals and reptiles.
Importance of Littoral Zone
This zone is also important in the world’s economy. A recent study has estimated that over 80% of the world’s fisheries are found in the littoral zone; this means that the zone must be protected from threats so that it can continue to provide fish for human consumption.
This zone is also home to an estimated 1 million people. In India alone, this zone accounts for more than 50% of the country’s coastal area. The littoral zone provides many jobs and also acts as a tourist attraction in many parts of the world, including in countries such as India and China.
The littoral zone is also crucial for providing a habitat for people who live in coastal areas. A growing distribution of coastal populations is due to the growth of human populations in the mid-latitudes. The coastal zone is also important because of the ecosystem services it provides.
It is an important framework for the development of human settlements. The littoral zone can be used for agriculture and aquaculture and tourism and leisure activities.
Threats to the Littoral Zone
The main threat to the littoral zone is pollution from sewage, oil, gas leaks, and the discharge of other hazardous materials. In some areas, it has been suggested that the zone may be unsuitable for human habitation because of the high levels of the population living there.
The zone is also susceptible to natural disasters such as tsunamis, which can cause huge damage to manmade structures in the zone.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The littoral zone is not always considered to be a threat to humans. In some parts of the world, such as the United States and India, there are large businesses located in and around the zone. These businesses make use of the zone for their activities, such as fishing and tourism.
The littoral zone is also experiencing other environmental conditions, which are affecting its ecology. Chronic pollution is one of these conditions. The main sources of pollution are sewerage plants, industrial wastes, and runoff from roads and domestic yards.
The littoral zone, like all other zones, is experiencing a high rate of biodiversity loss. Although the littoral zone may not always be threatened by human interference, it does experience risk factors. These can include land-use changes and other human activities.
The littoral zone also contains many areas with significant human populations that directly affect its ecology. The area around human settlements may also be subject to pollution, which can be caused by industrial discharges, vehicular emissions, and domestic wastewater sludge.
Each of these factors can lead to changes in the natural habitat of animals within the zone.
The littoral zone is also subjected to other threats, including those that come from natural disasters. The littoral zone can be subject to natural disasters such as flooding and tsunamis. The frequency of these events may increase as a consequence of global warming.
Littoral Zone Plants
In addition to this, the littoral zone also supports many commercially important species of plant. These plants are used in a number of ways and include:
The Littoral zone contains an abundance of fish species. Some of them are commercially important, while others may be more useful for their aesthetic value. Examples include:
There is a significant number of species found only in the littoral zone. The majority of these represent marine invertebrates, including both flora and fauna.
Many different types of algae are found in the littoral zone. A few of them are commercially important. In addition to this, the littoral zone also supports an abundance of microorganisms. These are responsible for a number of different ecosystem functions.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Littoral Zone Characteristics
The flora within the littoral zone consists of plants with a range of various characteristics. These may be habitat-specific, invasive, or new species which humans have introduced in recent times.
The fauna found in the littoral zone includes animals that are dependent on the sea for at least part of their life cycle.
There are a number of invasive species found in the littoral zone, including many microorganisms. These organisms have either been deliberately introduced by humans or accidentally brought in on vessels and other marine structures.
Many different plants and animals live within this area of the world and are important for a range of different reasons.
The size of the littoral zone varies with location. In general, however, it is very large compared to other areas of the world, with most part of it being shallow enough to require little effort in order to grow plants.
The littoral zone contains a wide range of habitats, from coastal dunes, mangroves, and salt marshes to mudflats and coral reef flats. In order to support life in such a range of conditions, the littoral zone contains a number of specialized habitats which, although they may appear similar at first glance, are actually very unusual.
The most obvious habitat in the littoral zone is that provided by rocky shores. These comprise areas of bare rock interspersed with areas of vegetation. Where the rock is close to the surface, it may be covered by a layer of mosses and liverworts, but in other places, rock-dwelling lichens such as “Pelagonium” may grow on it.
Where the coasts are composed of cliffs, erosion can result in a wide variety of landforms: from steep-sided stacks to sea stacks and arches to ‘Durdle Door’ in Dorset.
In the United Kingdom, sea cliffs are known as a barrier to navigation and can be very dangerous for shipping. Rocks at the base of a cliff are called the “Pillars of Heracles,” after the mythical hero who had to remove them in order to use Kalydonian Boar.
Rockpools, or tide pools, are depressions that form in sheltered areas of rocky coastlines. They are formed when the force of water splits rock or when dead rock becomes separated from the shore.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Tide pools tend to be found on coasts that have wide tidal ranges and exposure to storms and strong winds. They are very common in coastal regions with a temperate climate. The relatively shallow nature of these pools allows a wide range of creatures to be supported.
On rocky shores, seaweed can provide some shelter for juvenile fish and crustaceans. This habitat is exploited in the commercial extraction of edible seaweed, and the more delicate growths are also used decoratively in the horticulture trade.