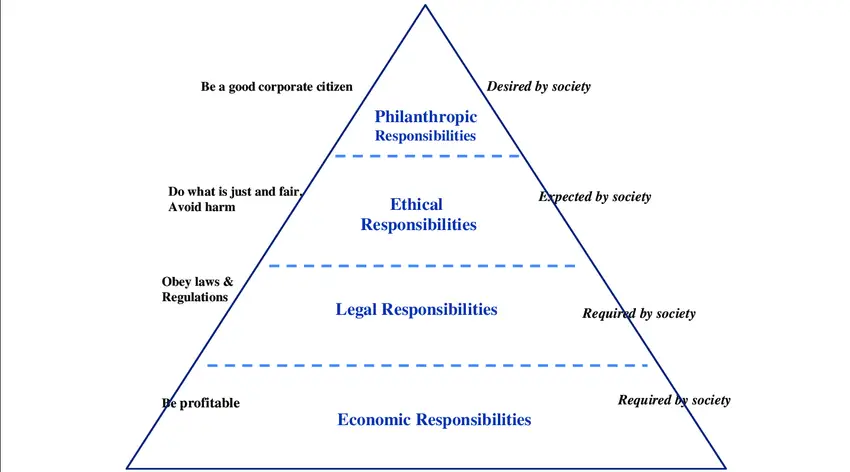
Archie Carroll’s CSR Pyramid | Corporate Social Responsibility Pyramid
Archie Carroll created a useful framework called Carroll’s CSR Pyramid to define and classify different kinds of corporate social responsibilities. Carroll’s Corporate Social Responsibility Pyramid involves a business’s conduct, and that business should be economically profitable, law-abiding, ethical, and socially supported.
In 2012, Dr. Carroll was awarded the first Lifetime Achievement Award in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) by the Institute of Management, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany.
Carol’s CSR Pyramid balances the self-interest of business with the wider, more virtuous organization’s needs, which is more socially responsible. To be socially responsible, they mean that profitability and obedience to the law are foremost conditions when discussing the firm’s ethics on the extent to which it supports society.
Although this theory is developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s, probably more pertinent today than ever to have been increasing social pressures for organizations to operate in a highly socially responsible manner.
Today, most businesses adopt the stakeholder theory meaning that companies try to balance shareholder interests with other stakeholders’ interests like customers, employees, and suppliers.
Archie Carroll’s CSR Pyramid
The Carrolls Pyramid has four components, namely:
- Economic responsibilities.
- Legal responsibilities.
- Ethical Responsibilities
- Philanthropic responsibilities.
Economic Responsibility
Its economic responsibility list concerns being profitable. It is the responsibility of a business to produce goods and services needed by society to make a profit.
Companies have shareholders who demand a reasonable return on their investments. They have employees who want safe and fairly paid jobs, and they have customers who demand quality products at a fair price.
It just means profit-making. Examples of economic responsibilities include:
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
- Providing shareholder returns.
- Keeping unit costs down.
- Lower unit costs.
- Trying to maximize sales.
- That sort of thing.
If this is lacking, the rest of the pyramid falls apart. The organization has to generate profits to survive otherwise, and the other practices just won’t happen. The economic unit is the base of the pyramid, where all other layers rest upon.
Legal Responsibilities (Obeying the Law)
The legal responsibility of businesses demands that they abide by the law and play by the game’s rules.
Should companies choose to bend or even ignore their legal responsibilities, then the retribution price could be quite high. Businesses have to ensure that they act within the law created by the state. Think about employment law or health and safety law.
At this level, the organization has to ensure that it meets all of its local legislative requirements, including consumer law, environment law, competition law, and many others.
The company meets these needs; it meets the needs of its customers’ environment on employees, particularly stakeholders.
After all, a business needs to maintain a positive relationship with its internal and external stakeholders.
Ethical Responsibilities (Do No Harm)
Ethical responsibility consists of what is generally accepted by society open above the economic and legal expectations.
They are not necessarily imposed by law, but they are expected from the public or governments of ethical companies.
Business behaves ethically when it’s acting in a fair and just way without infringing on people’s moral rights. Sometimes ethical responsibilities are not protected by the law. Examples of ethical responsibility include avoiding harm to the environment, are being open and fair to customers and suppliers, even if you’re not legally obliged to behave nicely.
That is going beyond just the pure basic legal requirements. So, if the organization is making decisions for itself about what is right and wrong. And ethics is about that level of morality.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
In the U. K. For example, supermarkets have recently self-imposed a minimum age requirement for the energy drink.
In the takeaway coffee market, many coffee shops are now offering quite significant discounts to consumers to bring their cups rather than using non-degradable cups, which causes pollution.
To this degree, the ethical need is starting to think more about consumers for society’s greater good.
Philanthropic Responsibilities (Discretionary)
This is being a good citizen. Discretionary responsibility is purely voluntary and guided by the company’s desire to make social contributions not mandated by economics, law, or ethics.
Discretionary activities include generous philanthropic contributions that offer no payback to the company and are not expected.
Philanthropy is the desire to do good to others, including spending money on good causes.
Meeting philanthropic responsibilities can involve active contribution to the community on improving people’s quality of life.
At this level, organizations are now actively taking measures to give something back. Rather than just trading appropriately, they’re trying to make a material impact and give something back to society.
Examples of Google, which spent over a million dollars providing 15,000 U. K school Children with the Raspberry Pi. Brand One water, whose sole mission is to take profit and reinvestment community projects in Africa, build wells for clean, healthy drinking water.
You will see more of these in CSR Report, where organizations are trying to participate in the community project.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
This level of the triangle focuses very much on the needs of stakeholders as the community.
Conclusion
.In summary, Carol’s CSR Pyramid is about the firm’s obligation, responsibilities beyond profit to actually giving something back to society and, importantly, full stakeholder. An important point is an economic aspect that must be paramount; nothing is built above without it. Any missing levels will be very difficult for an organization to realistic reach other levels.