Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand Example & Income Elasticity of Demand
Price Elasticity of Demand
What is Price Elasticity?
Price elasticity is the measure of how much the quantity demanded or supplied changes in response to a change in price. Price elasticity is a useful economic tool that helps businesses and economists understand the market for a particular product.
What is Price Elasticity of Demand?
The price elasticity of demand is a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded a good or service is to changes in its price. P rice elasticity can be calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price.
If the resulting number is greater than one, then that means an increase in demand when prices increased; if it’s less than one, then there was a decrease in demand when prices increased; and if it equals 1, then there was a decrease in demand was no change at all.
This responsiveness can be measured on a scale from zero (inelastic) to infinity (perfectly elastic)
Generally, for goods where demand’s price elasticity is less than one, demand is considered inelastic. This means that the demand for these goods will not increase significantly with a price decrease. Alternatively, goods with a price elasticity of demand between one and infinity are considered to have elastic demand.
Good price elasticity is the main determinant of how much a consumer will buy an item. If price changes, consumption will change. Costlier items are generally inelastic, and cheaper items are generally elastic.
A classic example is a toothpaste. As the price goes up, demand goes down and vice versa. It can be difficult to work out an item’s effective elasticity, but as a rule, items that are necessities are inelastic, and items considered luxuries are elastic.
What are the determinants of demand?
The determinants of demand are the most important factors in determining how much demand for a product or service will change in response to a change in price.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
There are six major determinants of demand. These are explained below.
1) Price– The price of the good influences demand in two ways: Firstly, it influences the potential consumptions, and secondly, it influences the amount of consumption in any given time period (the time period may vary between two weeks to two months).
2) Substitution effect– The greater the demand is for good and the more readily available it is, the more we will purchase. This is known as ‘simplifying’ or ‘optimizing.’ If a consumer has to purchase one product instead of another, then he/she will not buy the other product.
3) Income– Higher-income provides consumers with an opportunity to purchase more of a good. This means that more people can purchase a good than otherwise.
4) Income elasticity of demand– This is a measure of how responsive a good is to an increase or decrease in income. An income elastic demand describes the quantity demanded of the good as a function of an “increase in income.” Higher dependence on income would indicate that more goods and services will be purchased at any one time. Inversely, lower dependence on income would indicate that fewer goods and services will be purchased at any one time.
5) Time– A good or product will experience higher or lower demand at any given time. If a consumer is getting ready for a big event (ex. study, graduation, etc.), then the demand for that good will be high and vice versa. Also, if consumers expect the price of a good to increase (ex. petrol prices), they will purchase less and vice versa.
6) Expectations– All of the other things being equal (the strength of an economy, etc. ), consumers will purchase more or less of a good if it is priced, expected to be rise or fall. For example, if a good (ex. petrol) price is rising, many consumers will attempt to reduce their expenditure by purchasing lesser quantities of the good and/or substitute other goods.
The theory of demand also assumes that people will not increase their consumption if they expect a lower income in the future, which occurs with an increase in interest rates as there is less incentive for saving money. This is known as the interest rate effect.
Price Elasticity of Demand
What is Price Elasticity of Demand?
Price elasticity of demand measures how a price change will influence the total quantity demanded for a good or service. It is a measure of responsiveness in quantity demanded of a good or service to its price changes.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
In other words, it measures how much the quantity demanded for a good or service changes when there is a price change. If consumers are not responsive to changes in prices, then demand is said to be inelastic. On the other hand, if demand is responsive to changes in prices by a significant amount, then demand is said to be elastic.
Therefore, price elasticity of demand shows the relationship between changes in price and quantity demanded of a good or service. It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price.
Factors affecting the price elasticity of demand
Consumers’ Preferences
Several factors influence the price elasticity of demand for a good or service. For example, consumers’ preferences for that particular good or service and their incomes are two important factors.
Preferences refer to the degree to which consumers acquire, not just want, and consume a good or service. In other words, it refers to whether consumers really need and want a product. Thus, it refers to the degree of satisfaction with the consumption of a particular good or service.
Goods or services people do not want but still buy anyway are called substitutes for consumers. Examples include ice cream and movie tickets. People who have different preferences for a good or service may be willing to purchase more of it when its price falls. This type of consumption is called demand elasticity as a substitute.
Tastes also influence the price elasticity of demand. For example, a consumer may prefer one type of wine over another kind because they find the taste better, more pleasing, or simply different. In such cases, the taste of a wine is a substitute for other goods and services.
As a result, the price elasticity of demand for that particular wine is greater than that expected if the consumer had no preference for that particular wine. For this reason, tastes are important when determining the price elasticity of demand.
Income Changes
Income is another important factor that influences the price elasticity of demand. Consumers with higher incomes generally have more and different kinds of goods and services they can afford to purchase, as compared to consumers with lower incomes.
For example, a poor consumer may not be able to purchase an expensive car or private school for their child even though these are substitutes for them because these products are beyond their amount of disposable income. On the other hand, a rich consumer may be willing to pay a lot of money for these products because he can afford them and other expensive luxury items.
Price changes will influence the maximum amount that a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service. When consumers with higher incomes are faced with lower prices, the demand for these types of goods and services increases because they can now afford them. Therefore, it is necessary to use income as an independent variable when calculating demand and supply elasticity for goods and services.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Changes in incomes also affect the price elasticity of demand. If a person becomes more wealthy, they will be able to purchase more and different types of goods and services. This leads to a higher demand for those goods and services. A change in income can also cause changes in the market for a good or service.
For example, if a consumer gains enough income to afford an expensive car, that person will probably buy it because they need it. This could lead to a higher demand for that car as people are now willing to pay more for it than before. Changes in income also affect the price elasticity of supply.
If a producer receives enough income to produce more of a good or service, then he will probably supply it and earn more money from its sales than before. This could lead to a lower price for that good or service because the producer earns more money. Therefore, an increase in income leads to an increase in the price elasticity of supply for goods and services.
Availability of Substitutes
The availability of substitutes is also an important factor when determining the price elasticity of demand. For example, if consumers face a high price for beef and cannot afford to buy it, they will probably purchase chicken instead. This leads to a decrease in the demand for beef and an increase in the demand for chicken.
Therefore, consumers can substitute one product or service for another when deciding on which product or service to buy. If consumers can find substitutes, they are likely to select them during times of high prices for goods and services.
Time period
The time period that consumers have to react to changes in the price of a good or service also influences demand elasticity. For example, a consumer may purchase a washing machine if they have enough money to buy it. He or she may wait a while before purchasing it because the price that he or she paid for the washing machine will depreciate over time.
Therefore, there are two time periods involved in this example: Now and next year (i.e., 1 year from now). The purchase may be made when prices are low or when no other alternative is available. In the last instance, the price elasticity of demand for a good or service is greater.
Other factors
Other factors that influence price elasticity of demand include the amount of money consumers have to spend on a product or service, the novelty and desirability of a product, and how best it can be stored (e.g., in an attic). Many factors can influence the price elasticity of demand for goods and services.
Several economic theories of demand or supply help explain the price elasticity of demand. The income-expenditure theory explains the price elasticity of demand by looking at the effect that the changes in quantity demanded a good or service have on money value. This theory states that if a good or service becomes more affordable, then people will buy it. If a good or service becomes unavailable, then people will be willing to buy less of it.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The substitution effect states that if a good is less expensive (e.g., substitutes available), then the quantity demanded of a good increases. If more money is spent on something that does not have to be used for a long time, people will buy more of it.
The income effect says that if a good or service price decreases due to an increase in income, then the quantity demanded increases. People will purchase more when they are able to afford to at lower prices.
The law of demand states that if the price of a good increase, then the quantity demanded decreases. This is because when the price of a good increase, the cost of that good in terms of other goods and services increases. If it costs too much money to buy something, then people will not buy it. This relates to elasticity because, with high price elasticity, consumer demand has a greater effect due to price changes.
Income Elasticity of Demand
Demand is influenced by factors such as price, consumer disposable income, population size, and the rate of inflation. The price elasticity of demand measures how a change in the quantity demanded is influenced by a change in its price. It is calculated as:
In other words: demand is a function of income and inflation; elasticity represents what proportionate change an increase in income will cause to total demand. Elasticity is positive if the demand decreases with an increase in income and negative if it increases with an increase in income. So, if demand for a product is constant, demand will decrease with a rise in price and vice versa.
Income elasticity of demand formula
The substitution elasticity measures the proportionate change in quantity demanded resulting from a change in the price of one of the products used to produce the good being analyzed.
The formula for calculating income elasticity of demand is the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income as shown below;
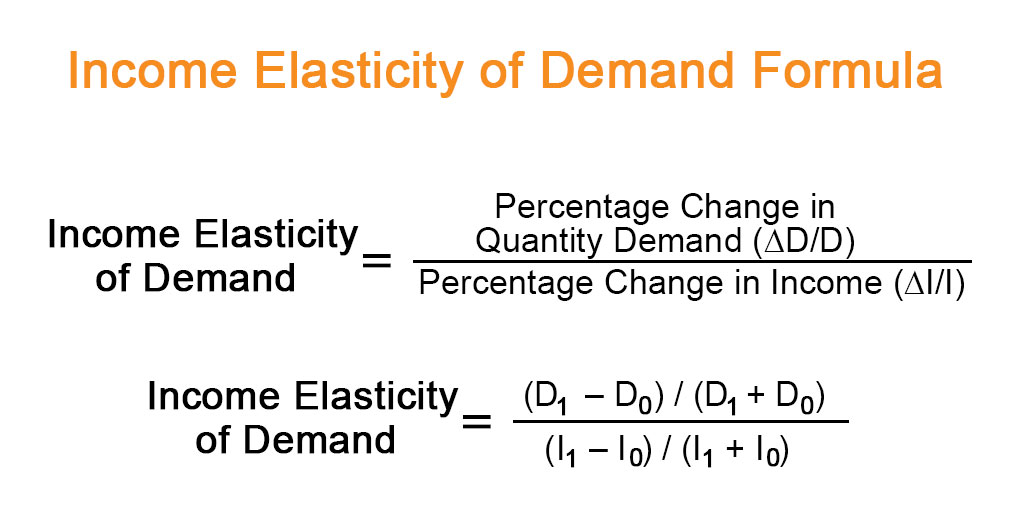
where,
D0 = Initial Quantity Demanded
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
D1 = Final Quantity Demanded
I0 = Initial Real Income
I1 = Final Real Income
If the demand for a product is elastic, producers will be able to charge prices high enough to cover costs and make a profit. Conversely, if demand is inelastic, the price charged will need to be low enough to reduce the number of sales necessary to make a profit.
The income elasticity of demand measures the proportionate change in quantity demanded, resulting from increased consumer disposable income.
Positive income elasticity of demand
Positive income elasticity of demand means that as people’s incomes rise, they purchase more goods and services. This is because when people have higher incomes, their purchasing power increases.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
A positive (or “normal”) response means that there is an increase in demand for a good when people’s incomes rise; this implies that goods are normal goods.
Positive income elasticity of demand Example
An example of an item with positive income elasticity would be gasoline because it is considered to be a necessity, and its price does not fluctuate much.
Negative income elasticity of demand
Negative income elasticity of demand refers to a situation in which demand for a commodity decreases with a rise in consumer income and increases with a fall in consumer income.
A negative (or “inferior”) response means that there is a decrease in demand for a good when people’s incomes rise; this implies that goods are inferior goods.
Negative income elasticity of demand graph
The graph below shows the Negative income elasticity of the demand graph.
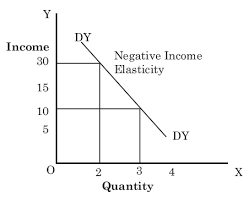
Negative income elasticity of demand Example
Negative income elasticity of demand is associated with inferior goods; an increase in income will lead to a fall in demand and may lead to changes to more luxurious substitutes.
Note
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
If income elasticity is negative, it means that demand will fall in response to a rise in income; if it is positive, demand will increase with an increase in income.
In other words: if demand for a good increase as incomes increase, the income elasticity of demand is positive. If it decreases, the income elasticity of demand is negative. Price elasticities can be used to analyze the effect of different factors on total industry output and international trade.
The income elasticity of demand measures the proportionate change in quantity demanded, resulting from increased consumer disposable income.
Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand Example
Let’s take an example. if a person experiences an increase in income from 10 to 20, and the quantity demanded a good reduced from 3 to 2, then the income elasticity of demand be calculated below


= (2– 3)/(3)/ (30-20)/(30)
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
= (-1/3)/10/30
= -1
This would make it an inferior good.
An inferior good has an Income Elasticity of Demand < 0. This means the demand for an inferior good will decrease as the consumer’s income increases.
Examples of goods with elastic demand
A good example of a product with elastic demand is gasoline. Gasoline prices change often and quickly. If gas prices are high in a given month, then fuel-efficient cars will be popular. Conversely, if gas prices are low in a given month, then SUVs will be popular.
Examples of goods with perfect elastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand is a demand that will change proportionally to the change in quantity being supplied.
One of the perfect examples of a good with perfectly elastic demand is airplane seats. If prices of tickets go up, airlines will start flying fewer airplanes, which will, in turn, mean fewer seats and a higher supply. If prices go down, airlines will fly more airplanes, which means more seats and a lower supply.
Examples of goods with inelastic demand
Inelastic products are defined as ones where a change in price does not significantly impact demand for that product.
For example, bottled water is a product that has inelastic demand. Consumers usually are not as sensitive to price fluctuations of this product and will purchase it regardless of the price change.
Another example is a diamond necklace that is worth $10,000 would have a very inelastic demand as the price is so high that most people could not afford it. In comparison, a $10 necklace would have elastic demand because the price is low enough that most people would buy it.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.