John Kotter Change Management Model
John P. Kotter’s eight-stage process for creating major change is one of the most widely recognized models for change management. John P. Kotter is a retired Harvard Business School professor of leadership. Kotter is also a co-founder of Kotter International, based in Seattle and Boston.
Kotter’s article about the eight-stage process for leading change was originally published in the spring of 1995 in the Harvard Business Review.
Leaders and the guiding coalition use the Kotter eighth step Change Model to anchor change in organizational culture. It is a series of actions needed in each step and pitfalls to be avoided to implement the necessary change in the organization successfully.
Kotter Change Model Summary
Professor Kotter has proven over his years of research that following the eight-step process for leading change will help organizations succeed in an ever-changing world.
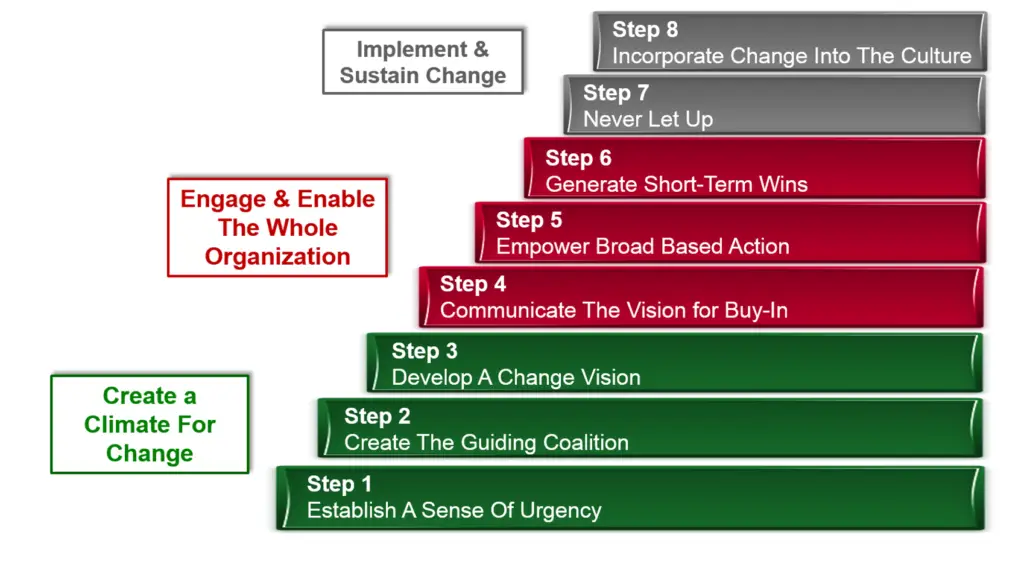
In general, the model consists of three main phases. These phases cover eight individual steps. They are sometimes also called stages.
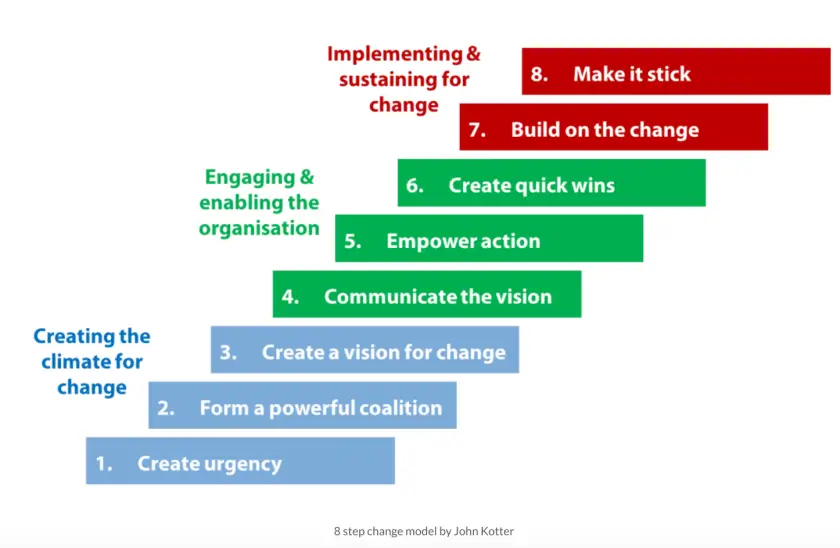
Phase One, which covers the first three steps, is about creating a climate for change and getting a shared understanding of the difficult assignment which lies ahead of the organization.
Phase Two, which covers steps four through six. It is about engaging the employees in the process of enabling the employees to affect change in the organization.
Phase Three, which covers the last two steps off the eight steps. It is about implementing and sustaining change in the organization.
John Kotter suggests that for change to be successful, at least 75 % of a company’s management needs to “buy into” the needed change. It basically means that the organization needs to work really hard on Step 1 of the process and spend significant time and energy building urgency before proceeding to the next steps.
Each step is necessary when you want to transform your organization to give your transformation effort the best chance of succeeding. You have to take the right actions at each stage and avoid common pitfalls.
Kotter’s 8 Step Change Model of Implementation.
Step 1: Establishing A Sense of Urgency
The first step is establishing a sense of urgency;
Actions are needed in this stage;
- You have to examine the market and competition for potential crises on untapped opportunities.
- You have to convince at least 75% of your managers that the status quo is more dangerous than the unknown.
Pitfalls in this stage:
- Executives sometimes underestimate how hard it can be to drive people out of their comfort zones.
- Management can also become paralyzed by risks.
- A transformation of the organization requires leadership from executives.
Step 2: Forming Powerful Guiding Coalition
Step two is about Forming a powerful guiding coalition.
Action needed in this stage;
- You have to assemble a group with a shared commitment and enough power to lead the change effort.
- You also have to encourage them to work as a team outside the normal hierarchy.
- A major transformation generally demands activity outside of formal boundaries, expectations, and protocol.
Pitfalls in this stage;
- No prior experience in teamwork at the top level of the organization.
- Top management appoints team leadership to a person without enough power. No matter how capable or dedicated the team members are groups without strong line leadership never achieve the power required to change the organization.
Step 3: Creating A Vision
Step three is about creating a vision.
Actions needed in this stage:
- The team has to create a vision to direct the change effort.
- The team also has to develop strategies for the realization of the vision.
Pitfalls in this stage:
- Presenting a vision that’s too complicated or too vague to be communicated in five minutes. If you can’t communicate the vision to someone in five minutes or less and get a reaction that signifies both understanding and interest, you are not done.
Step 4: Communicating the Vision
Step four is communicating the vision.
Actions needed in this stage;
- Use every possible way to communicate the new vision and strategies for achieving it. The vision will be referred to in emails, in meetings, in presentations; it will be communicated anywhere and everywhere.
- Teach new behaviors by example of the guiding coalition. If the vision focuses on the environment, the management has to drive more environmentally friendly cars. Executives have to walk the talk professionally and privately.
Pitfalls in this stage;
- The Guiding Coalition is under communicating the vision.
- A single memo announcing the transformation or even a series of speeches by the CEO and the executive team are never enough. Actions speak louder than words. Nothing undermines a communication program more quickly than inconsistent actions by leadership.
Step 5: Empowering Others To Act On The Vision
Step five is empowering others to act on the vision.
Actions needed in this stage;
- The guiding coalition has to remove or alter systems or structures undermining the vision.
- An organization that claims to want to be a customer focus finds its structures fragment resources and responsibilities for products and services. They have to change this toe, unleash people to do their best work.
- The coalition has to encourage risk-taking, and nontraditional ideas, activities, and actions, realigning incentives on performance appraisals to reflect the change vision can profoundly affect the ability to accomplish the change vision.
Pitfalls in this stage;
- Failing to remove powerful individuals who resist the change effort. They may not actively undermine the effort, but they are simply not wired to go along with what the change requires. Easy solutions to this problem don’t exist.
Step 6: Planning for And Creating Short Term Wins
Step six is planning for and creating short-term wins.
Actions needed in this stage;
- The guiding coalition must define and engineer visible performance improvements.
- Running a change effort without attention to short term performance is extremely risky. For leaders in the middle of a long-term change effort, short term winds are essential.
- Getting these wins helps ensure the overall change initiatives’ success; the leaders must recognize and reward employees contributing to those improvements.
Pitfalls in this stage;
- Failing to score successes early enough,
- management is leaving.
- Short term success is up to chance.
- Short term winds rarely simply happen.
- Short term successes are 12 to 24 months into the change effort.
- We are planning for short term winds, not praying.
Step 7: Consolidating Improvements On Producing Still More Change
Step seven is consolidating improvements on producing still more change.
Actions needed in this stage;
- Leaders must use increased credibility from early wins to change systems structures and policies, undermining the vision.
- They also have to hire, promote and develop dedicated employees who can help them implement the vision.
- Leaders also have to reinvigorate the change process with new projects and change agents.
Pitfalls in this stage;
- Celebrating a win is fine; declaring the war won can be catastrophic until changes sink deeply into a company’s culture, a process that could take 5 to 10 years.
- New approaches are fragile and subject to regression.
- Ironically, it is often a combination of change initiators and changes resistors that create the premature victory celebration.
- In their enthusiasm over a clear sign of progress, the initiators go overboard, allowing resisters to convince troops that the war has been won; the useful changes that have Been introduced slowly disappear if nobody is pushing the change forward,
Step 8: Institutionalizing New Approaches.
Step eight is institutionalizing new approaches.
Actions needed in this stage;
- Leaders must articulate connections between new behaviors and corporate success. They must show employees how the new approaches, behaviors, and attitudes have helped improve performance.
- Change sticks when it becomes the way we do things around here.
Pitfalls in this stage;
- Management is not creating new social norms and shared values consistent with changes.
- They are promoting people into leadership positions who don’t personify the new approach.
Kotter 8 Step Change Model Diagram
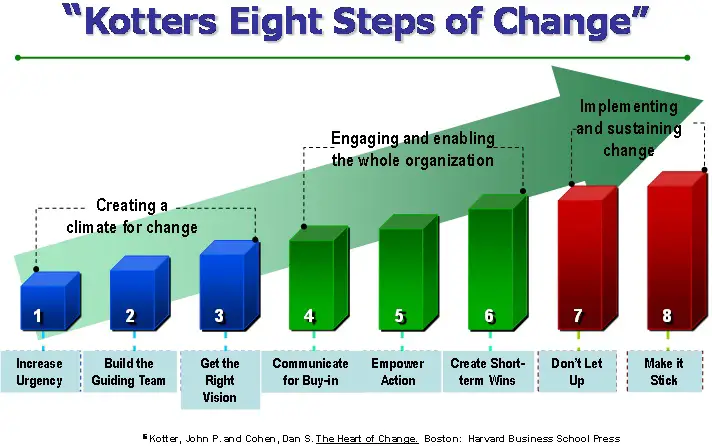
Kotter Change Model Example
Anchoring New Approaches in the Culture
A review of examples using Kotters Eight Steps Model with a manufacturer of high-pressure valves.
The founder of the company, who was an ingenious engineer, died a long time ago. Today, the company is a major player in the industry, and they are still living by the founder’s mantra.
We deliver solutions before the customer knows he has a problem.
-Current Mantra
In recent years, the company has had problems. The company has lost market share, and they have made losses in the last two years.
The new CEO wants to address the problem by using Kotter’s eight steps to solve the problem.
Step One
The new CEO has established a sense of urgency.
His message is clear.
The existence of the company is threatened.
-CEO’s Messege
He also makes it public in the staff magazine that the company has lost an important customer to back this message.
Step Two
CEO forms a powerful guiding coalition with himself as a leader. He knows he has to assemble 20 to 50 important persons from the organization with shared commitment and enough power to lead the change effort.
He knows that a major transformation generally demands activity outside of formal boundaries, expectations, and protocol.
Therefore, he hires consultants from Kotter International and invites the key customer to participate in the coalition.
A market survey shows that the company’s brand reputation is high, but the products have become too expensive, and the products contain too much in different functionality.
Step Three
In Step Three, the guiding coalition has to create a relatively easy vision to communicate and appeals to both the internal and external stakeholders.
The coalition wants to change the old mantra into a vision centralized around the customer.
The new vision is ;
we invent jointly with our lead customers.
-New Vision
The team also has to develop strategies for the realization of the vision.
Step Four
In Step four, the guiding coalition has to communicate the vision to the organization’s employees and external stakeholders.
All the members of the coalition have to communicate the same message anywhere and everywhere.
The CEO and other executives have to visit customers to participate in fairs, where customers come instead of Tech Fairs.
They also have to prioritize the marketing and sales department.
Executives have to walk the talk externally as well as internally.
Step Five
In Step Five, the coalition encourages executives and employees from different departments to contact customers.
The top management changes the rules about contacting and working together with customers.
Before, it was only the key account manager who had contact with the customer. Now the rules have changed.
Employees from the logistics department, RD department, and other departments are encouraged to contact their counterparty in the customer’s organization.
The company is shifting from key account management, butterfly leveraging to diamond collaboration with the customer. The role of the key account manager is totally changed.
Management will have to lay off those who resist the change vision.
Step Six
In Step Six, the guiding coalition has to announce some short-term wins. The CEO goes public with a new product developed jointly with one of the lead customers.
The product development phase only took 12 months, which is twice as fast as normal.
The materials of the new product are recyclable, and the production costs are cut by 30%. This is due to the fact that all departments have optimized together in partnership with the customer.
The CEO publicly recognizes and rewards the employees who have contributed to the success with the strategy of developing new products together with the customer.
Step Seven
In Step Seven, the guiding coalition must use the increased credibility from the win in Step six to change other conditions, undermining the vision.
Their next battle to win is to integrate their value chain would lead customers and share big data.
Some executives do not want this openness with the customers. They will try to stall further developments in this direction. Therefore, the Guiding coalition has to reinvigorate the change process again and again.
They have to win a lot of battles before the war is won.
Step Eight
In the eighth and last step, leaders must create new social norms and shared values consistent with changes.
They have to promote people into leadership positions who personify the new approach.
They just want to work together with customers. They have to see them as allies.
The company has reached the vision when leaders and employees do not behave differently in terms of whether it is a colleague or a partner from a customer they are working together with.
The war is won. Now it is time for a new vision and a new beginning at Step one.
What are the Disadvantages /Criticism of Kotter Change Model
- It is a rigid approach that you can only take one step at a time. Some scholars argue that you can have eight different speeds in an organization. The vision is the same, but the changes happen at different speeds in different parts of the organization.
- Some steps are not relevant in some contexts. A simple example is the replacement of major software used to process operations or the change of equipment on a manufacturing line. In these cases, the changes are often irreversible, and steps seven and eight might not be relevant.
- Dealing with difficulties during change. According to Kotter’s framework, management planning changes should limit those obstacles, but the model is not detailed enough to provide help in all scenarios.
- Kotter’s timeframe is measured in years. Short term winds are within 12 to 24 months. The circumstances may have changed radically before all eight steps have been completed.
The model gives you an overview of the different steps in a change process in an organization on that there is a logical path through a change process. The model shows you what conditions to consider during a change process.