Marshall Lerner Condition in Economics
What is Marshall-Lerner’s condition in economics?
Marshall Lerner Condition refers to the proposition that the devaluation of a country’s currency will improve its balance of trade with the rest of the world only if the sum of the price elasticities of its exports and imports is greater than one.
For example, if total export revenue falls due to inelastic demand for a country’s exports and total import expense rises due to inelastic demand for its imports, this will further worsen the country’s trade deficit.
.
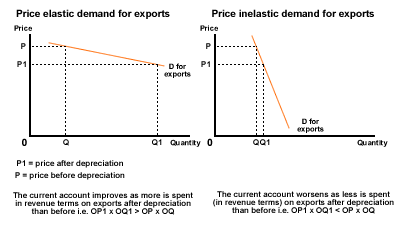
So devaluing its currency may not always be the best way forward for a country looking to reduce its trade deficit.
The depreciation of a currency will increase import prices and decrease export prices. Therefore, the more price elastic the demand for imports and exports, the greater will be the fall in demand for imports and the increase in demand for exports, and the greater will be the improvement on the current account.
The Marshall-Lerner condition is named after British economist Alfred Marshall and Russian economist Abba P. Lerner.
The Marshall-Lerner condition is an economic principle that states that a country’s imports should exceed their exports by the amount of any trade deficit.
This means that if a country has a trade surplus, it will buy more from other countries than they buy from it. If this isn’t the case, then there is no incentive for international trade to occur.
How is Marshall-Lerner’s Condition Met
The Marshall–Lerner condition is met when the absolute number of a country’s export and import demand elasticities (demand responsiveness to price) is greater than one. If it is fulfilled, and if a nation starts with a zero-trade deficit, then when the country’s currency depreciates (e.g., it takes less yen to buy a dollar), the country’s balance of trade would increase (e.g., the U.S. will develop a trade surplus with Japan).
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Because of the shift in relative prices, the country’s imports become more costly, and exports become cheaper. The Marshall-Lerner situation means that the indirect impact on the quantity of exchange would outweigh the country’s direct effect of paying a higher price for its imports and obtaining a lower price for its exports.