Robert Solow Growth Model
The Solow model is a neoclassical growth model developed by Robert Lucas Jr in the early 1970s. This model’s goal was to explain why some countries, like Japan or Germany, were previously impacted hugely by WWII had better postwar growth than other countries. In WWII, the capital stocks of Germany and Japan were substantially reduced. Hence, they started the postwar years with low amounts of capital. As they added capital, they grew faster than the U.S., which emerged from the war with our large capital stock intact.
The Solow Growth Model is one of the most important papers in economics and has been a major influence on all economic growth models since. This model can be applied to any country, as well as to small regional economies.
The Solow Growth Model is a valuable tool in analyzing the economic growth of an economy. It explains long-run economic growth as a function of increases in productivity, capital accumulation, and labor or population increase.
Robert Solow Growth Model Graph
Implication
The Solow Growth Model predicts that the poorer country will grow faster in the long run if their population, savings rate, and capital depreciation rates are equal.
Solow’s model shows that increasing the savings rate could get an economy to a higher output level after the increase, but the long-run rate of economic growth wouldn’t increase.
Doubling the savings rate would increase a country’s GDP per capita but wouldn’t change the fact that the economy would grow at the same rate as before. But a “technological” advance boosts our long-run growth rate.
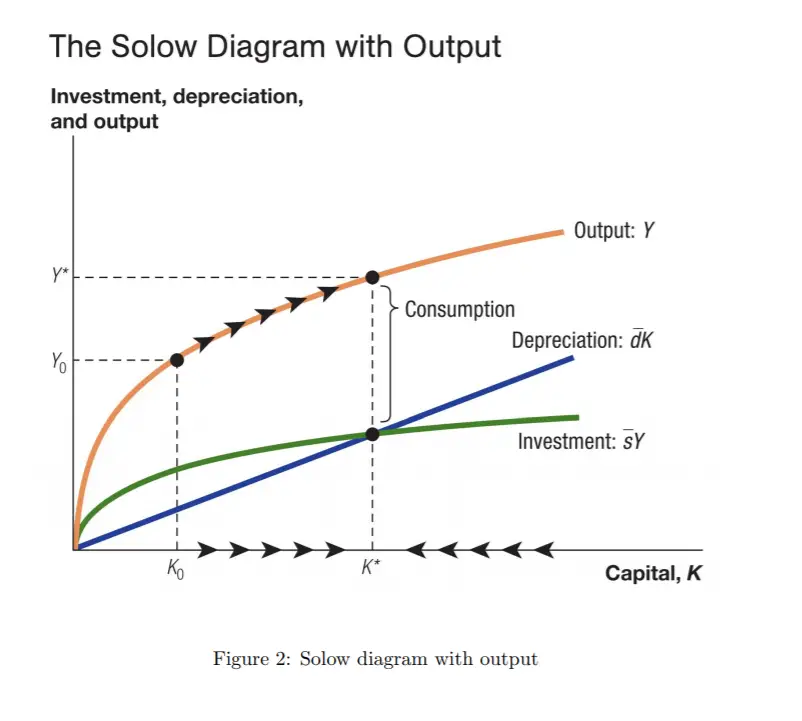
At k*, the amount of new investment per effect worker exactly balances the need for breakeven investment, so k is stable: k = 0. At this level of k, the economy has settled into a steady state in which k will not change.
A ‘steady-state growth path’ is reached when output, capital, and labor are all growing at the same rate, so output per worker and capital per worker are constant
Neo-classical economists believe that to raise the trend rate of growth, and it’s necessary for there to be an increase in the workforce and increased productivity from both workers and capital.
Conclusion
Solow’s growth model is a macroeconomic theory that states economic output results from capital accumulation and technological progress.
Solow’s model is important for guiding how we are thinking about economic growth in the real world. For example, once you understand the Solow model, you realize a country like China growing much faster than the United States isn’t surprising.
China is experiencing catch-up growth as it invests more in its economy and adopts technology and other resources from richer countries. Eventually, China will catch up to the technological frontier and grow at about the same rate as the United States. At least in the long-run.
A ‘steady-state growth path’ is reached when output, capital, and labor are all growing at the same rate, so output per worker and capital per worker are constant