Neobehaviorism Definition and Neobehaviorism Examples
Neobehaviorism Definition
What is neo behaviorism?
Neobehaviorism is a psychological theory that emphasizes the role of observation and imitation in the learning of behavior, with a focus on behavioral conditioning and cognitive processes.
It is considered to be the second phase of behaviorism, as developed by figures such as B.F. Skinner, Clark Hull and Edward C. Tolman.
What is Behaviorism?
Behaviorism is a psychological approach that examines human behavior and mental processes, focusing on the impact of external stimuli on responses. It is a field of study in psychology that investigates how humans respond to environmental stimuli.
One principle of behaviorism is “stimulus generalization,” which describes how a stimulus can lead to a similar response or pattern in another organism. Behaviorists argue that this principle explains why some individuals respond better to praise than others.
Neobehaviorism Pavlov and BF Skinner
Neobehaviorism, a branch of psychology that studies the use of reinforcements and punishments to shape behavior, has gained renewed interest in the 21st century.
It is associated with the work of B.F. Skinner and other psychologists who did not follow the theories of Ivan Pavlov, who first studied conditioning through experiments with dogs.
Neobehaviorism has been applied to both animal behavior in natural environments and human behavior in clinical settings for over a century.
Four key aspects of neobehaviorism include behavioral objectives, reinforcement schedules and ratios, positive punishment, and negative punishment.
Neobehaviorism Tolman and Bandura
Tolman and Bandura, both neobehaviorists, conducted research on the behavior of animals in laboratory settings to gain insights into how their behavior is influenced by the environment.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Tolman focused on how the environment shapes behavior, while Bandura examined the concept of modeling behavior and its impact on other members of the same species.
One example of their experimentation is when rats were placed near food and their whiskers were touching it, they started eating without looking at or using their nose, suggesting that sensory input plays a role in shaping eating habits in both rats and humans who are exposed to various stimuli.
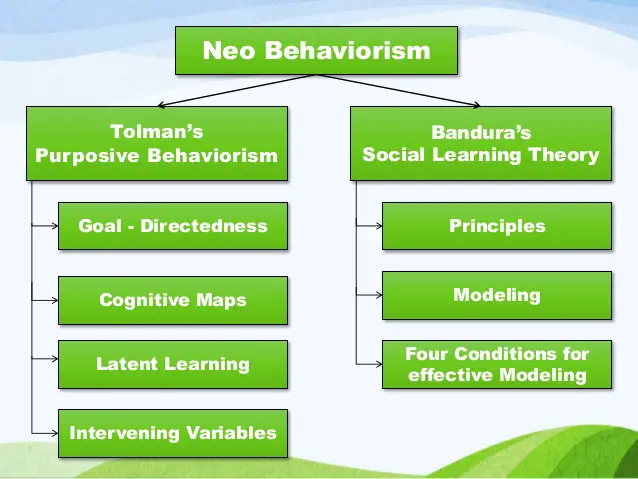
Tolman and Bandura, researchers in the field of neobehaviorism, held differing views on the motivation behind behavior.
Tolman believed that individuals are motivated by what is most important to them, while Bandura’s theory posits that individuals are motivated by goals that can be achieved.
To test these theories, they conducted an experiment in which rats were presented with two buttons: one that immediately dispensed food pellets, and another that released them after an eight-second delay. Some rats were given access to both buttons, while others only had access to one.
The results of the experiment showed that when given a single option for obtaining food, the rats would find ways to make themselves more comfortable before pressing the button, while those with access to both options often became frustrated due to the difficulty in choosing one
Neobehaviorism Example
Neobehaviorism is a psychological approach that holds that the environment shapes behavior through associations between stimuli and responses.
It emphasizes the use of rewards and punishments, rather than explanations or reasoning, to modify behavior.
One example of neobehaviorism is the use of operant conditioning to train animals. Operant conditioning involves an animal learning to behave in certain ways in order to receive a reward or avoid punishment.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Shaping, a type of operant conditioning, involves gradually rewarding an animal for progressively closer approximations of a desired behavior.
Another example of neobehaviorism is extinction, where rewards are withdrawn for a specific behavior, with the goal of eventually eliminating it.
Additionally, positive reinforcement, a principle of classical conditioning, is also used in neobehaviorism, where a stimulus is paired with a response to establish an association between them.
Neobehaviorism in Learning Today
Neobehaviorism, as applied in education, aims to understand the factors that contribute to successful learning, and how to apply them in the classroom.
It can assist teachers in developing individualized plans for students, leading to greater success for both the individual student and the class as a whole.
Some specific applications of neobehaviorism in education include the use of self-talk as a way to regulate behavior, creating a learning environment that promotes success through the use of positive reinforcement and clear instructions, and setting clear expectations and providing feedback to students to help them determine what works best for them.
Difference Between Behaviorism and Neobehaviorism
What are the Differences and Similarities Between Behaviorism and neo-behaviorism?
Behaviorism and Neobehaviorism are both psychological approaches that study human behavior, but they have distinct differences and similarities.
Behaviorism focuses on the environment and how it shapes behavior through conditioning or reinforcement. Neobehaviorism, on the other hand, is a more modern approach that considers internal factors such as thoughts, feelings, and desires.
Behaviorists believe that all behaviors are learned through conditioning or reinforcement, while Neobehaviorists believe that some behaviors may be innate, but most are learned through experience.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Behaviorism is a school of psychology that focuses on observable actions and the study of stimulus-response connections. Neobehaviorism is an extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the importance of mental processes in understanding human behavior.
Behaviorism is a psychological theory that behavior can be studied as an objective phenomenon and it studies the relationship between stimulus and response to understand how environmental factors influence behavior.
Neobehaviorism, on the other hand, is a branch of psychology that studies human behavior in terms of its physical properties, such as neural activity or muscle movements.
What are the Similarities between behaviorism and neobehaviorism?
Behaviorism and Neobehaviorism share some similarities, such as their focus on observable behaviors and the fact that both approaches were developed by psychologists.