Porter Diamond of National Advantage | Porter Competitive Advantage Model
Michael Porter Theory of Competitive Advantage
History of Porters Diamond Model
Michael Porter’s the Diamond Model was published in 1990 in his book The Competitive Advantage of Nations. It is a model that can help us understand why a nation becomes the home base for successful international competitors in a particular industry and other nations don’t.
He argues that the old theories proposed by Adam Smith and David Ricardo are not sufficient to explain competitiveness between technology advantage in today’s nations.
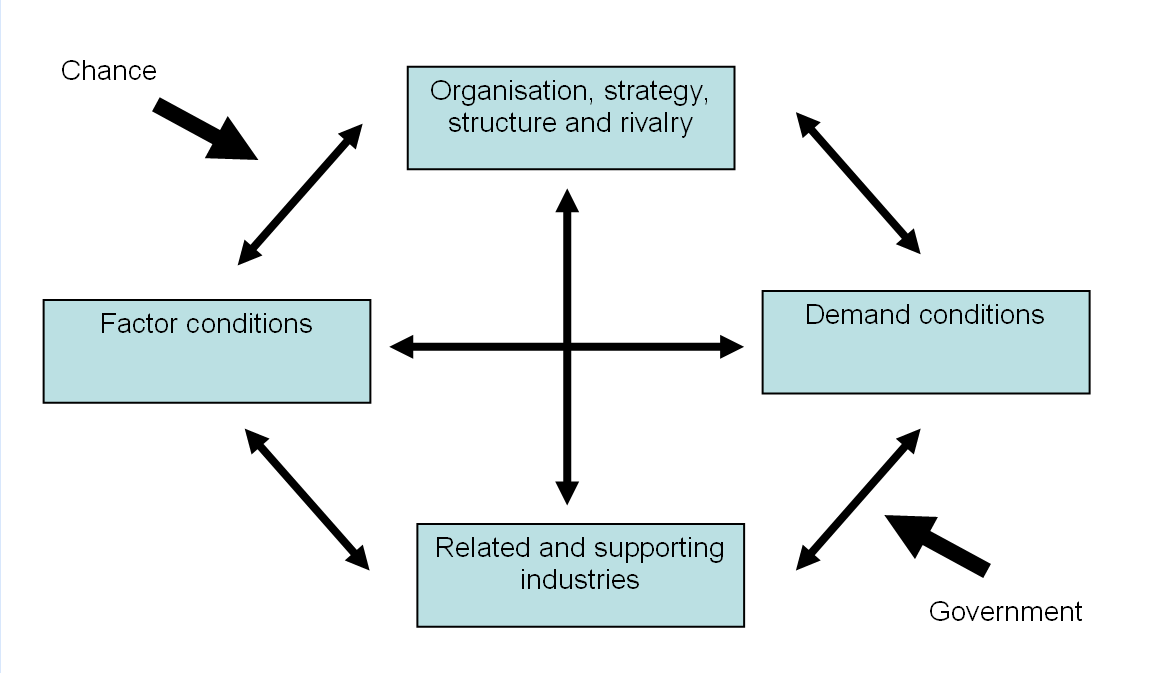
In this diamond model, the regional advantages can be assessed by four factors, which include;
- Firms Strategy and Rivalry,
- Demand Conditions
- Related and Supporting Industries And
- Factor (Input) Conditions.
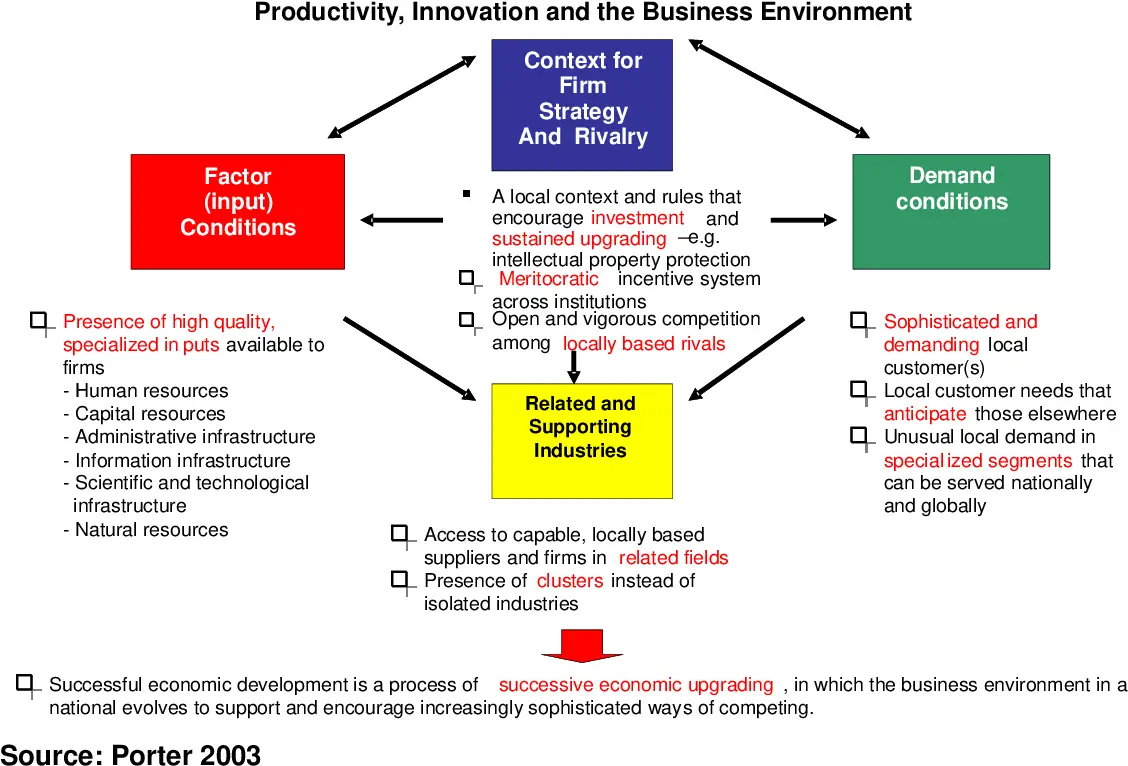
This is a graphical representation of Porter’s Diamond showing how the four factors interact. The model also points out that two additional determinants influence the four main determinants. These are government policy and the role of chance events.
Factor (Input)Conditions.
Factor (input) conditions are the factors of production that include skilled labor, education, capital, climate, and infrastructure.
The factors most important to competitive advantage in industries in advanced economies are not inherited but are created within a nation. To understand the role of factors in competitive advantage, it is necessary to distinguish between types of factors.
Advanced and Basic Factors
The first demarcation is between advanced and basic factors. Advanced factors of production are skilled labor, knowledge, capital, and infrastructure.
Any company can obtain basic factors such as unskilled labor and raw materials on do not generate a competitive advantage.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Specialized and Generalized Factors.
The second distinction is between specialized and generalized factors. Specialized factors involved narrowly skilled personnel infrastructure with specific properties, knowledge bases in particular fields, and other relevant factors to a limited range or even to just a single industry.
Examples could be a scientific institute with expertise in optics, a port specialized in handling bulk chemicals, or a pool of venture capital seeking to fund software companies,
Germany has possessed a competitive advantage in automobile production for many years because the nation has advantageous factors through its highly educated personnel, such as graduate engineers and computer scientists, and the industry has specialized factors. They have highly skilled workers trained in specialized apprenticeship programs and graduates from special university programs.
Demand Conditions
The second broad determinant of national competitive advantage is demand conditions.
Demand condition is a country with sophisticated home buyers that have been aware and demand for advanced quality and innovative products, which can create international competitiveness.
The main factor is home demand conditions, which influence nearly every industry.
Home Demand
The composition of home demand shapes how firms perceive, interpret, and respond to buy a need. Nations gain a competitive advantage in industries where the home demand gives local firms a clearer or earlier picture of buyer needs than foreign rivals can have.
Size of the Market
It is not merely the size of the market that is important, but it is the intensity and sophistication of the demand that is significant for competitive advantage. If consumers are sophisticated, they will make demands for sophisticated products, which will help produce sophisticated products.
Gradually, the country will achieve a competitive advantage in such production.
Early Market Saturations
As significant as early home market penetration is early or abrupt saturation. Early saturation forces companies to continue innovating and upgrading, and finding international markets for their products.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
In consumer electronics products, the Japanese home market’s saturation is rapid, and product life cycles are extremely short.
This is because buyers have homogeneous tastes combined with sophistication and status consciousness. This combination gives them a competitive advantage in comparison with foreign rivals.
Related and Supporting Industries
Related and supporting industries are the imports for a company with drives success; for example, raw materials from fabric supplies in Italy help drive the fashion Milan industry’s success.
Supplies Industries
The presence of internationally competitive supplier industries in a nation creates advantages in downstream industries.
It gives efficient, early, rapid, and sometimes preferential access to the most cost-effective inputs.
The benefit of home-based suppliers may be found in the process of innovation and upgrading firms gain quick access to information to new ideas and insights, and supplier innovations.
Related Industries
The presence in a nation of competitive industries that are related often leads to new competitive industries. Related industries are those in which firms can coordinate or share activities in the value chain when competing.
An example is pharmaceutical firms that use the same university when testing new drugs.
Firms Strategy Structure And Rivalry
Firm strategy and rivalry is the competition in the home market that drives innovation and quality. When there’s lots of competition and lots of rivalries, these keeps companies on their toes, and so they try to out-compete each other by continually developing more innovative and quality products and services.
Conditions of the Nation
Many aspects of the nation too numerous to generalize influence how firms are organized and managed.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Some of the most important aspects are attitudes towards authority, norms of interpersonal interaction, workers’ attitudes towards management and vice versa., social norms of individualistic or group behavior, and professional standards.
These, in turn, grow out of the educational system, social and religious history, family structures, and many other unique national conditions.
Goals
Sharp differences exist within and among nations in the goals that the firms seek to achieve and their employees’ and managers’ motivations.
Domestic Rivalry
Domestic rivalry creates particularly visible pressure on each other to improve. Vigorous local competition sharpens advantages at home and precious domestic firms to sell abroad to grow.
Governmental Policy; Government on Porter’s Diamond Model
There are also times when the government could also influence a regional advantage. It influences all four of the determinants through various regulatory and deregulatory measures.
Influence the system
Policies implemented without consideration of how they influence the entire system of determinants are likely to undermine national advantage as they enhance them.
Government influence on Factor Conditions
Government effects factor conditions in many ways. Among the most important government roles are creating and upgrading factors, whether they are skilled human resources, the basis for scientific knowledge, or infrastructure.
Among these factors, there is little doubt that education and training are decisive in national competitive advantage.
The fact is that world standards for workers, technical personnel, and managers are high and rising. No nation will prosper unless its citizens meet them.
Government influence on Demand Conditions
Government procurement can be a positive force for upgrading national competitive advantage if they provide early demand for advanced, sophisticated products or services from local firms.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
An example is the Danish government’s early decision to pay for hearing aids for those who needed them. This was an important reason for the international success of Danish firms in this industry.
Government influence on Unrelated and Supporting Industries
The government’s effect on unrelated and supporting industries. The government must support these industries in the same way as the industries that have the advantage. Government has an important role in nurturing and reinforcing clusters.
Government influence on Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry.
The government’s effect on firm strategy, structure, and rivalry. Government policy has numerous ways of influencing how firms are created, organized, managed their goals and how they compete.
Sustaining and enhancing competitive advantage requires that a nation’s firms take a global approach to strategy.
Government policy should seek to avoid currency restrictions, restrictions on foreign investment, and restrictions and the inflow and outflow of skilled personnel that impede internalization.
Few government arm roles are important to upgrading an economy than ensuring vigorous domestic rivalry, which requires strong antitrust policies because a dominant domestic competitor rarely results in international competitive advantage.
Chance Events
This is chance events are developments outside firms’ control over the nation’s government, such as pure inventions, breakthroughs in basic technologies, wars, external political developments, and major shifts in foreign demand.
They create discontinuities that can unfreeze or reshape industry structure and provide an opportunity for one nation’s firms to supplant and others.
Chance has played an important role in shifting competitive advantage in many industries. A shift that changed competitive advantage was the oil shock in 1970. The oil shock ultimately helped upgrade the Japanese industry because Japan was especially vulnerable to energy costs and took aggressive energy conservation steps.
Porter Diamond Model Company Example
The Diamond Model must be seen as a system. The effect of one determinant often depends on the state of others.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
An example where Porter’s Diamond came in use to explain a region advantage is in Germany’s luxury, high power car manufacturing industry for the brand.
The German automobile industry has a national competitive advantage. The industry has four major players. These are VW, BMW, Mercedes, and Opel, and they are all placed in the south of Germany.
Factor Conditions Porter Diamond Influence
The other determinants influence the factor conditions in different ways. Home demand influences the particular types of factors that are created in demand conditions. The German automobile buyers have sophisticated demand. They expect better on better cars.
This tends to channel social and private investments into related factor creation. They have well developed, specialized educational and scientific institutions geared towards the automobile industry in the south of Germany.
The pool of factors on the rate at which they are created is also shaped by the presence of related and supporting industries.
The automobile industry is supported by companies such as Bosch, and the IT company, SAP. These companies belong to industries that possess or stimulate their own mechanisms for creating and upgrading specialized factors.
Some of the factors are usually transferrable, such as ERP Systems from SAP.
A cluster of domestic automobile rivals stimulates factor creation. The automobile industry is viewed as prestigious in Germany; it stimulates the best job seekers to invest in gaining specialized skills.
Demand Conditions Porter Diamond Influence
The most important effect is probably domestic rivalry. Intense domestic rivalry creates home demand through product and marketing innovation.
The presence of successful related and supporting industries can also enhance international demand for German cars. The overall image of German products as high quality is also carried over to the car industry.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The internalization of home demand of high-end cars has a factor creating mechanism. The automobile industry will attract foreign students and firms, making training and education in Germany the industry’s Center for Innovation.
Related and Supporting Industries Porter Diamond Influence.
Factor conditions in the automobile industry, especially factor creating mechanisms, have influenced the development of related and supporting industries.
The universities in the automobile cluster will educate students on IT excellence, such as Computer-aided design & computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) with case studies from the industry.
Where home demand is significant, more and specialized supplies emerged to address unmet needs. An example is logistic companies dedicated to serving the automobile industry. They’re working more efficiently in developed German car channels around the world.
The concentration of rivals in the German automobile industry has led to the growth of thriving and a highly specialized group of supplier industries ranging from light bulbs, tires, brakes, different materials, composites, etcetera.
Firm strategy structure on rivalry Porter Diamond Influence influenced by the other three determinants.
Demand conditions enhanced rivalry in the automobile industry when demanding Home buyers continuously expect news from the car world.
The rivalry in the German automobile industry is almost personal. They all want to deliver the next wonder Car.
Related and supporting industries will deliver new ways of doing things to the automobile industry.
The factor conditions could nullify or reinforce the international advantages of the industry in Germany. Specialized factor creation mechanisms could spawn new entrance or usually startups in the industry.
One of the universities could be the source for an energy-efficient CO2 neutral high-performance car. This would, of course, affect the strategy of the firms in the industry.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Government and Chance Events Porter Diamond Influence
The change from petrol-driven cars to another energy source will create discontinuities that allow shifts in a competitive position.
It has the potential to nullify the advantages of the firms in the German automobile industry and creates the possibility that a new national car making industry might supplant them.
The government can support research in fields that helped develop a German energy-efficient CO2 neutral high-performance car.
Porter Diamond Model Analysis Example (Summary)
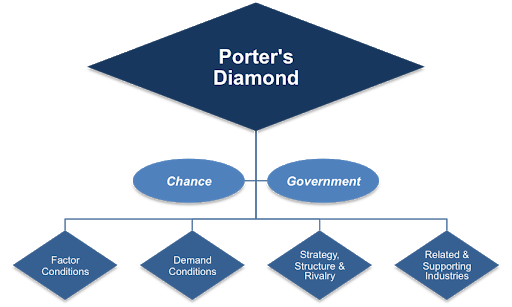
From the above, it is clear that Germany’s car manufacturing industry has a regional advantage because it satisfies the four key factors in Porter’s Diamond.
With first strategy and rivalry, we see strong rivalry amongst lots of car manufacturers, so they compete intensely and keep developing more innovative and quality products.
There are certain demand conditions amongst car buyers.
There are no speed limits in Germany, so the own sophisticated buyers what more powerful cars, therefore the industry, and develop innovative engines to care for this particular need.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
There are related supporting industries such as the iron and steel industry in Germany, which provides materials for the car manufacturers.
There is also a high level of education and training within the workforce. Banks also provide capital, and they’re also component supplies and IT infrastructure.
They’re also factor conditions, including skilled engineers from renowned universities and the government’s focus on scientific research, which helps to push the car manufacturing industry.
The government has played an important role in creating a regional advantage as it supported and funded scientific research launched the construction of more roads and canals in the 19th century.
By satisfying all these factors, in Porter’s Diamond, it, therefore, helps to explain why Germany’s luxury high power car manufacturing industry has a regional advantage.
Criticisms of The Porters Diamond Model.
- Porter feels that sizeable domestic demand must be present for attaining a competitive advantage. But some industries have flourished only because of demand from foreign consumers. An example is Nestle, the lion’s share of the earnings from which come from foreign sales.
- If the domestic suppliers of inputs are not available, the backward linkage will be meaningless as the determinant related and supporting industries don’t exist in that nation.
- The availability of natural resources, according to Porter, is not the only condition for attaining a competitive advantage. There must be other factors, but a study has shown that some Canadian industries emerged on the global map only on the basis of such natural resource availability.
Nevertheless, these limitations do not undermine the significance of porter’s national competitive advantage theory, especially in advanced industries located in advanced countries.