Burke Litwin Model of Organizational Change /Burke Litwin Causal Model
Burke Litwin Model of Organizational Change
Burke Litwin Model of Organizational Change was first published by George H Litwin and W Warner Burke in 1992. Burke Litwin Model of Organizational Change is also called the Causal Model of Organizational Performance and Change. It suggests linkages that hypothesize how performance is affected by internal and external factors.
Burke Litwin’s change Model provides a framework for assessing organizational and environmental factors that are keys to successful change. It demonstrates how these dimensions should be linked causally to achieve a change in performance.
The causal model links what could be understood from practice to what is known from research and theory. The model discusses how different dimensions relate to each other and discusses how the external environment affects an organization’s various factors.
Burke Litwin Organizational Change model focuses on providing a guide for both organizational diagnoses and planned, managed organizational change, one that clearly shows cause-and-effect relationships.
The model looks quite a complex model with those aspects all interlinked, and when there is a change in one particular area, it will impact all of the other areas in the business.
As indicated in the framework, the model has been color-coded. Three significant factors need to be considered.
Burke Litwin Causal Model
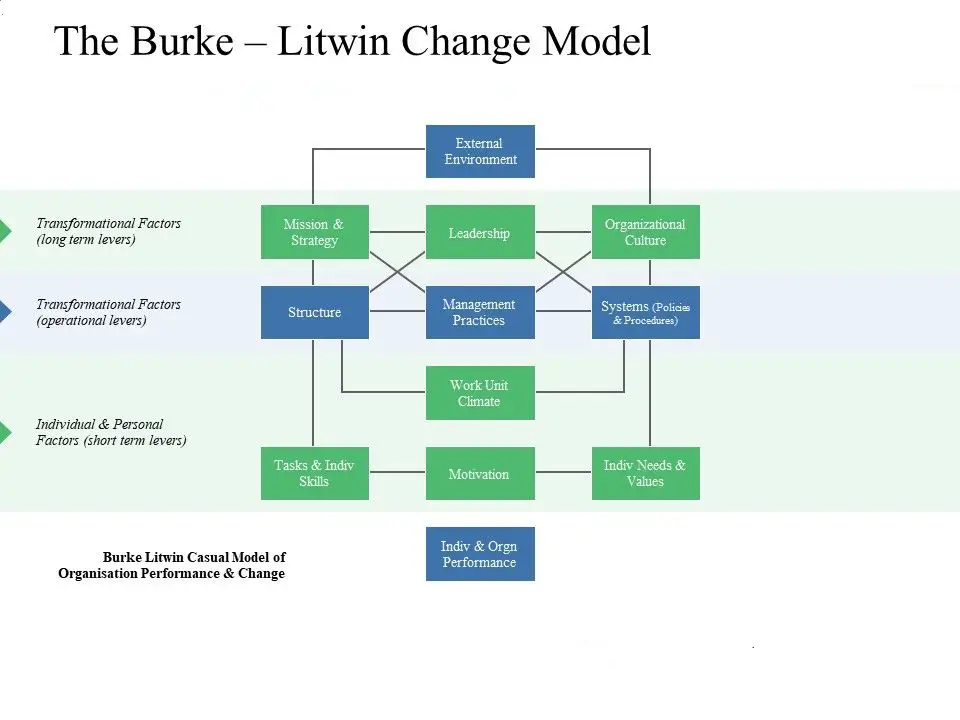
Burke Litwin Model of Organizational Performance and Change
- The transformational factors are the ones that are dealt with by the strategic management.
- The transactional factors are the aspects that need to be considered by operational management.
- The individual and personal factors of those which need to be looked at by staff management.
The External Environments
The external environment includes factors such as markets, legislation, competition, and the economy. All of these will have consequences for your business and you as the business leader. It is vital to identify issues that may affect you and your team—for example, the budget and business rates.
Mission and Strategy
A business’s mission articulates its reason for existing. The strategy sets out how the organization will go about achieving its mission.
It will be developed in light of environmental change, and you will need to understand the change in strategy and be able to communicate the implications to your staff.
Leadership
This considers the business attitudes and behaviors of you and your senior colleagues and how they perceive these behaviors as a whole.
How changes are implemented and accepted through the business will be largely influenced by yourselves.
Organizational / Business Culture
Business culture could be described as the way we do things around the organization. It considers the beliefs, behaviors, values, and conventions that prevail in your business.
Culture change does not happen overnight. It evolves as a result of any changes in your business. As a manager, you should keep in mind the business’s desired state in terms of how you expect people to behave and not to behave.
What your business values as important, you as a manager need to talk the talk and walk the walk.
Structure.
The changes in strategies can often lead to changes in the way that the business is structured. This can have an impact on relationship responsibilities and the ways of working.
Your job is to assess the impact of that structural change and ensure that your team understands why it is required and what it means for them.
Systems and Processes
The systems and processes that evolve over time and can result in red tape. It’s important to look at what’s being put into place to ensure it is still relevant and considered.
Do they meet the purpose of the legislation, the ethical and moral values of your business?
The Work Unit Climate
This considers employees’ perceptions of their immediate colleagues and working environments. The working environment is often what shapes our view of the business and influences the extent to which we feel satisfied in our jobs.
Changes to the immediate working environment need to be managed sensitively, as they are likely to invoke a range of emotional and political responses from staff.
Task Requirements and The Individual Skills and Abilities.
Changing the business will often require changing the work carried out on the skills available in the team.
You need to assess whether all the right skills or in place and if they can be developed, or if you need to bring them in from outside.
Individual Needs and Values
Changes to team membership convene a change in the team dynamics. It would be great in a perfect world if we could recruit exactly the exact fit for our teams and in terms, the style, abilities, and skills mix.
In reality, that’s not always possible, and it’s your job to identify any risks in this area and mitigate them as best you can.
Employee Motivation.
Employee motivation is about considering the significance of individual and organizational goals. Motivation is key to effective change.
The real challenge is maintaining motivation throughout any change period, particularly when change is not well received by those affected.
Individual and Organizational Performance
That’s the individual and organizational performance, which is affected by all of those aspects within individual and personal factors on the business as a whole.
Burke into Litwin’s theory requires you to ask a series of questions at each level. Based on the answers you get, you must decide what changes are required and develop a suitable implementation strategy.
Burke and Litwin identified that links into those.
External Environments
These are the political, economic, social, and technological developments that prompt change. The PESTEL analysis adds to more. The environmental and legislation
Strategic Management
The mission and strategy, leadership, and culture of the Power SWOT Analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats), but when you add power to it, you look at these strategies that come out from that SWOT analysis.
Operational Management
The business strategy canvas will help you link the mission strategies and culture, and leadership into your organization’s structure, systems, practices, and climate.
Staff Management
To have a big picture, you need a skill need analysis that sits alongside Greiner’s Growth model.
Burke Litwin Model Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Burke Litwin Model of Change
- Burke-Litwin’s Model of Organizational Change clarifies the key factors behind any change. It provides a useful framework for organizational change management in which to orient managers’ ideas and plans.
- Burke Litwin Model of Organizational Change integrates many major change factors.
- Burke Litwin’s causal model presents causal relationships as compared to many other models that are purely descriptive. The key factors in the model with the dependencies between them have a high practical value in practice.
- The model distinguishes between the set of variables that influence and are influenced by organizational climate and those influenced by organizational culture.
Limitations/Criticism and Disadvantages of Burke Litwin Model of Change
- Burke Litwin’s causal model is quite complex and could be difficult to analyze.
- The environmental factors that drive change are not always the case. Many organizational changes are triggered by internal factors or leadership and not the external environment.
- Many critics of Burke -Litwin model view that oversimplification of different change factors produces sub-factors, which actually makes it a more complex model.


