Macro Environment Analysis PESTEL | SWOT Analysis
What is Macro Environment Analysis?
Macro environment analysis is an important part of strategic management whereby business analyses outside environmental factors that influence business. These factors include; political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, and legal factors.
Macroeconomics is the external analysis of the structure, behavior, and decision-making of economies as a whole rather than individual markets.
The macro-environment is the economy as a whole and covers all factors affecting an organization indirectly.
Macro environments are concerned with the complete national economy and international economic systems. It examines phenomena such as;
- Changes in Employment
- National income rates of growth
- Domestic product
- Inflation and
- Price levels.
Macroeconomics’ objectives are to achieve full employment, grow the national income, real economic growth, price stability, and balance exports and imports.
External analysis
External analysis is used to evaluate environmental influences on an organization’s profitability. Once an organization has worked at its place in the market, it can focus on developing appropriate strategies.
Terms you should be aware of in macroeconomics factors include;
Macroeconomic Inputs
- Consumer Expenditure
- Investment Expenditure
- Government Expenditure
- Balance of Payments
Consumer Expenditure: Consumption is based on consumer’s consumption. It is determined by household incomes, the tax rate, and the proportion of household income saved.
Investment Expenditure: Business investment is an investment in capital items.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Government Expenditure: Government spending refers to spending on infrastructure, salaries of public servants, military purchases, and any investment expenditure made by the government.
Balance of Payments: Balance of payments represents the difference between an economy’s net import and export values. If exports are more than imports, then the balance of payments will be positive. If imports are more than exports, then the balance of payments will be negative.
Macroeconomic Outputs
- Gross Domestic Product
- Gross National Product.
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product is the market value of all goods and services produced within a country in a given time period. It could be measure as all expenditure used to buy goods and services produced or is all income earned from the production of goods and services.
Gross domestic product equals consumption plus investment, plus government spending plus the balance of payments.
Economic growth may be measured by the increase in the rial growth national product per head of the population. The principle being high gross domestic product leads to improved business activity.
Aggregate demand is an economy’s overall demand for goods and services. The formula for aggregate demand is
Aggregate demand equals consumer spending plus investment by firms plus government spending plus demand for exports, less demand for imports.
Changes in aggregate demand need to be taken into consideration when forecasting sales. The more stable a government, the easier it is for organizations to plan
Income and Expenditure Flow.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
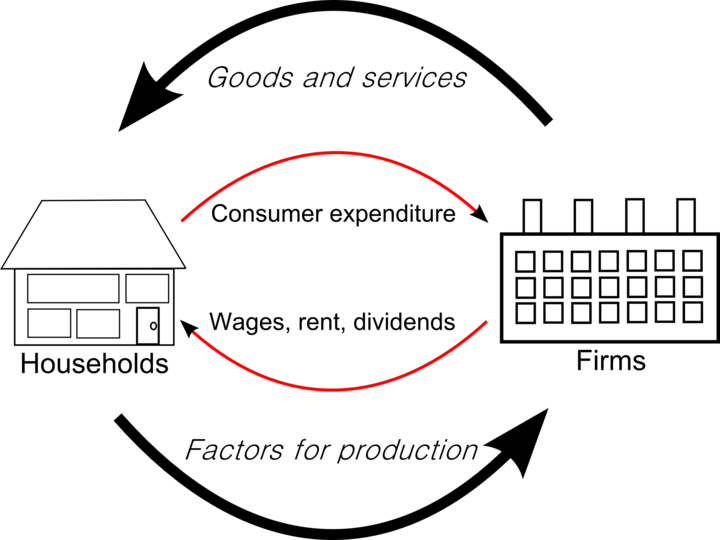
This is the circular flow of income in an economy. The circular flow of income is a model of the economy in which the major exchanges are represented as flows of money, goods, and services between economic agents.
The flows of money and goods are exchanged in a closed circuit and correspondent value but run in the opposite direction.
With this image of the circular flow of income, we’re assuming the economy has two sectors, firms and households.
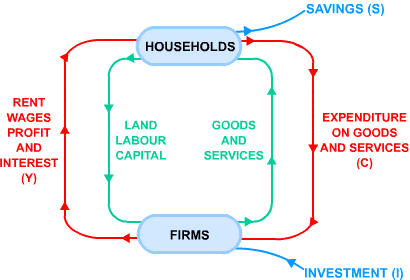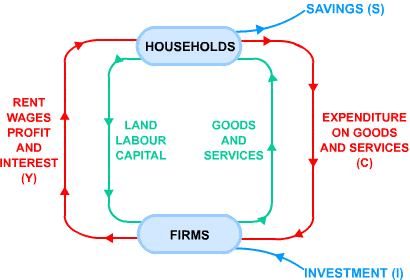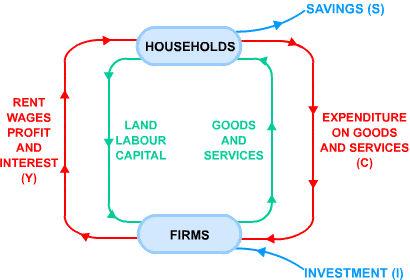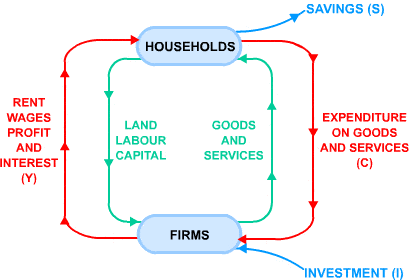
We need to add investment expenditure, government spending, and the balance of payments to the diagram.
Gross National Product
Gross national product (which is a total value of goods produced and services provided by a country during one year) equal to gross domestic product, plus the net income from foreign investments, gross national product equals consumption plus investment plus government spending plus the balance of payments plus net income receipts minus net payment outflow.
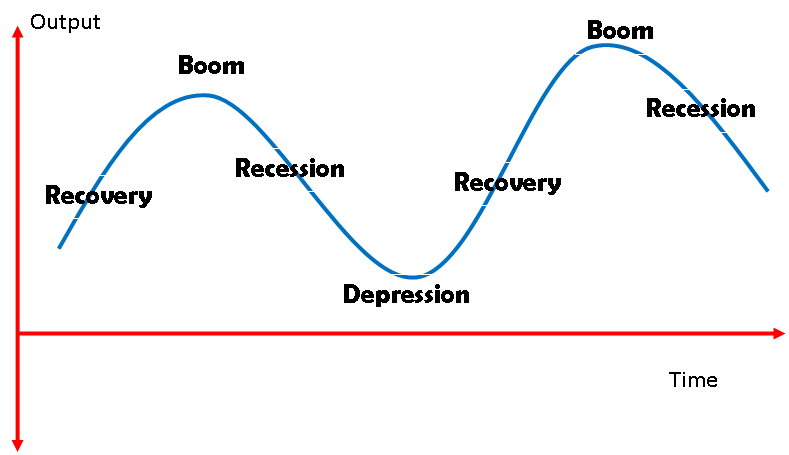
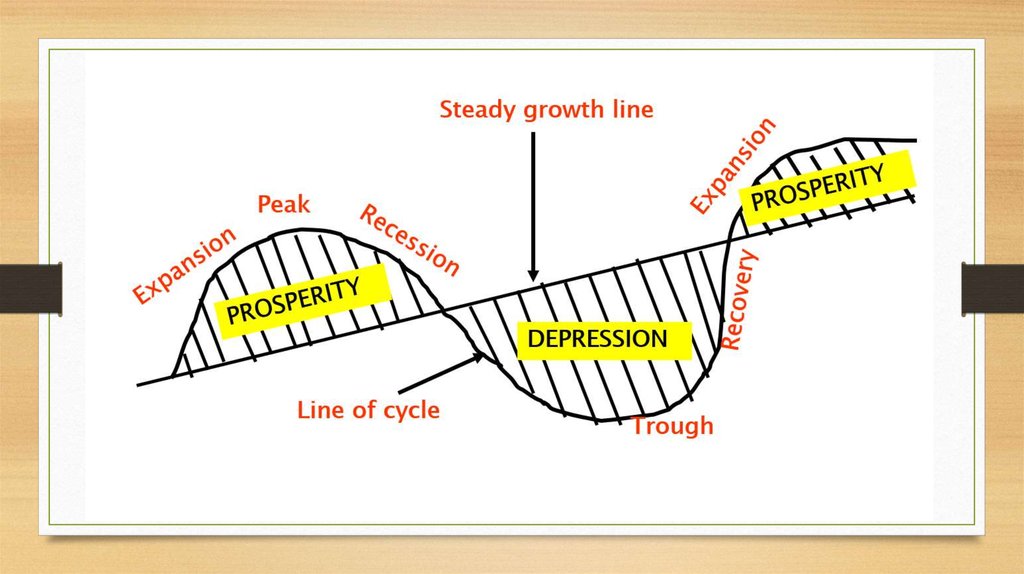
The Business Cycles.
The business cycle is the peaks and troughs and economic activity that an economy experiences over a period of time. It is basically defined in terms of a period of expansion or recession.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The phases of the business cycle are boom, recession, depression, recovery.
Boom Economy
Boom economy is an economy that is reaching its full capacity. It is a rapid economic expansion period resulting in higher gross domestic production, lower unemployment, and rising inflation.
Booms often lead to supply and demand shortages, which are often met by higher prices than more production.
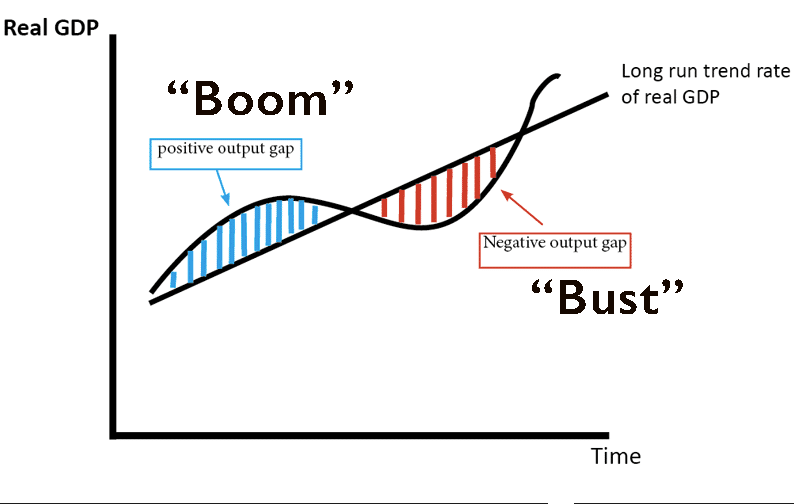
A bust Economy is the opposite of a booming economy. Economic growth decreases rapidly in a bust economy.
Recession
Recession is where there is falling demand in the economy. As household consumption decreases, organizations scaled down their outputs to match demand. This can lead to rising unemployment levels.
A recession definition is full in the country’s gross domestic product rate for two more or consecutive quarters.
Slump
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Slump or depression is a sustained long-term downturn in the economy. Aggregate demand is low, and Long term low consumer consumption leads to low business confidence and high unemployment.
Economic recovery
Recovery can be brought about through new technology entering the market, t the success of economic policies, increased volumes of investment, increased labor, supply rise in international trade, and the discovery of natural resources, to name but a few examples.
It is where economic aggregate demand is increasing. This leads to higher business confidence, which can lead to businesses starting to invest in the future.
Increasing employment and rising household incomes
Economic stagnation
Economic stagnation is a prolonged period of slow economic growth measured in the gross national product, usually accompanied by high unemployment levels.
Trade cycle.
This is a series of fluctuations in the rate of growth adjusted for inflation. For gross domestic product over its long-term trend
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Macro Environment Analysis PESTEL
PESTEL analysis
PESTLE analysis is a good way to look at macroeconomics in general. It is analysis is an external analysis that looks at the macro environment on its influence over organizational performance.
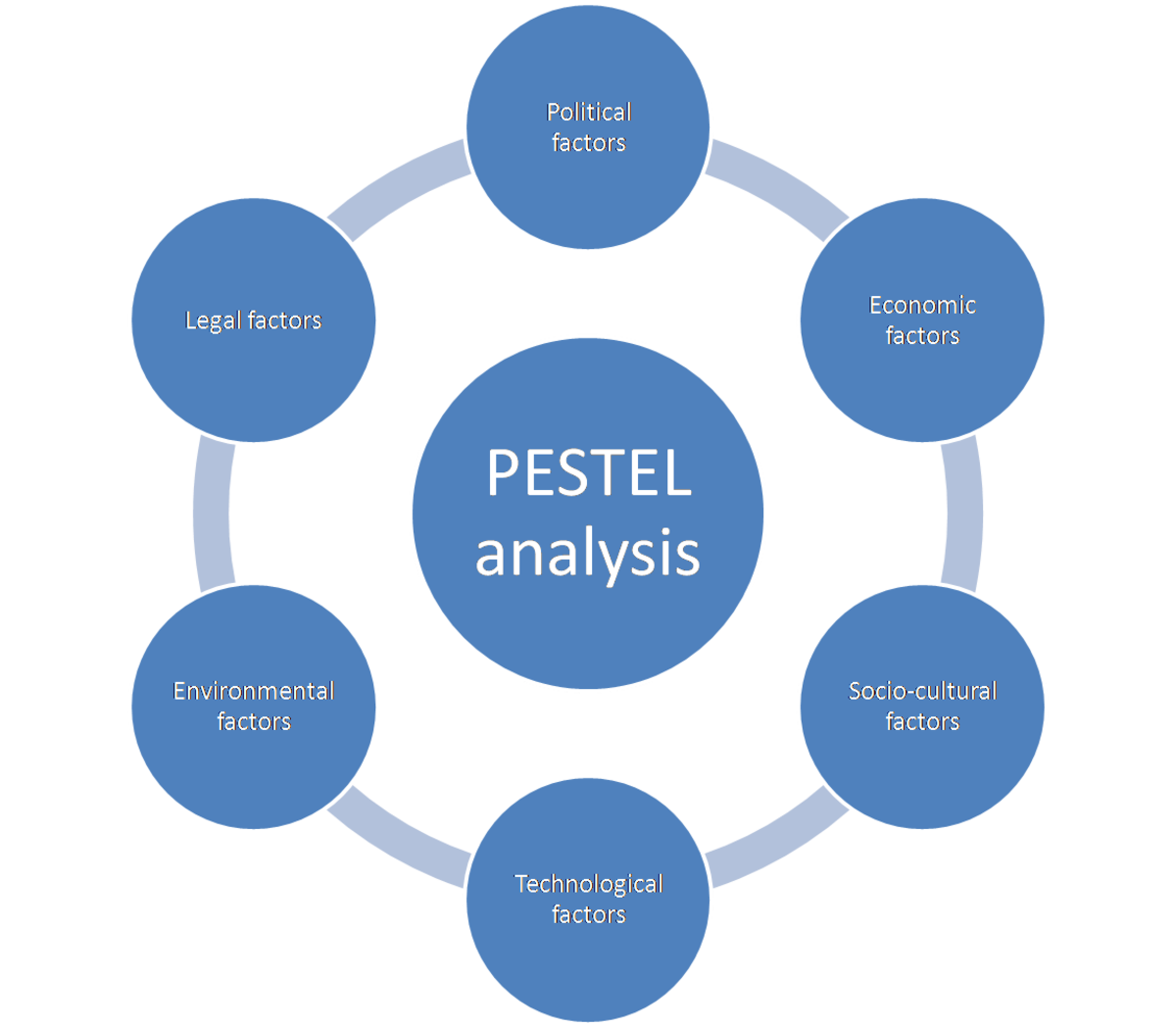
It stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal influence.
PEST analysis
You may also see the pestle analysis referred to as the PEST analysis. This is where environmental analysis is combined with social analysis on legal analysis is combined with political analysis.
Political Factors.
Political factors determine the extent to which the government may influence the economy or a certain industry.
They’re the role the government plays in the economy, covering political systems and ideologies.
The addition or removal of political regulation constraints composes major strategic threats or advantages for an organization.
Some examples of political factors are tax policies, the stability of government, government expenditure levels, foreign trade regulations,
Economic Factors.
These factors are determinants of an economic performance that directly impacts an organization on have resonating long term effects.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Economies are rarely in a stable state. This is due to changing economic factors such as investment levels, inflation, saving levels, consumer confidence, interest rates, and exchange rate fluctuations.
The government’s aim regarding macroeconomic policy is to provide full employment, price stability or low inflation, economic growth, and the balance of payments, which is the difference between a country’s imports and exports on the appropriate distribution of income wealth.
The macroeconomic policy focuses on the country’s overall demand for the national product, which is its outputs of goods and services.
The supply of production factors; labor, land, capital and entrepreneurship, government policy, and national expenditure.
The impact of economic factors, for example, are the likes of monetary policies, fiscal policies, inflation, and unemployment.
Social Factors
Social Factors scrutinize the social environment of the market. They’re known as demographic changes and look at the changes in the population of a country.
For example, social influences are population demographics, wealth distribution, education levels, and lifestyle changes and trends.
Technological Factors
These factors pertain to innovations and technology that may affect the operations, often industry or a market favorably or unfavorably.
Technological influences, for example, the likes of the speed of technological transfer, rate of obsolescence, new technological platforms,
Environmental Factors.
These factors include all those that influence or are determined by the surrounding environment.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
These are relatively new considerations for organizations effectively; they’re green issues, environmental influences like environmental protection
Legislation
legal factors, the addition or removal of legislative constraints compose major strategic threats or advantages for an organization.
Organizations need to know what changes in legislation are possible on what their impact will be.
The government’s legal systems relating to businesses provide a framework for organizations to do business. This framework provides organizations with stable conditions in which business can operate with confidence.
Legal influences include data protection law, consumer law, contract law, employment law, and health and safety law.
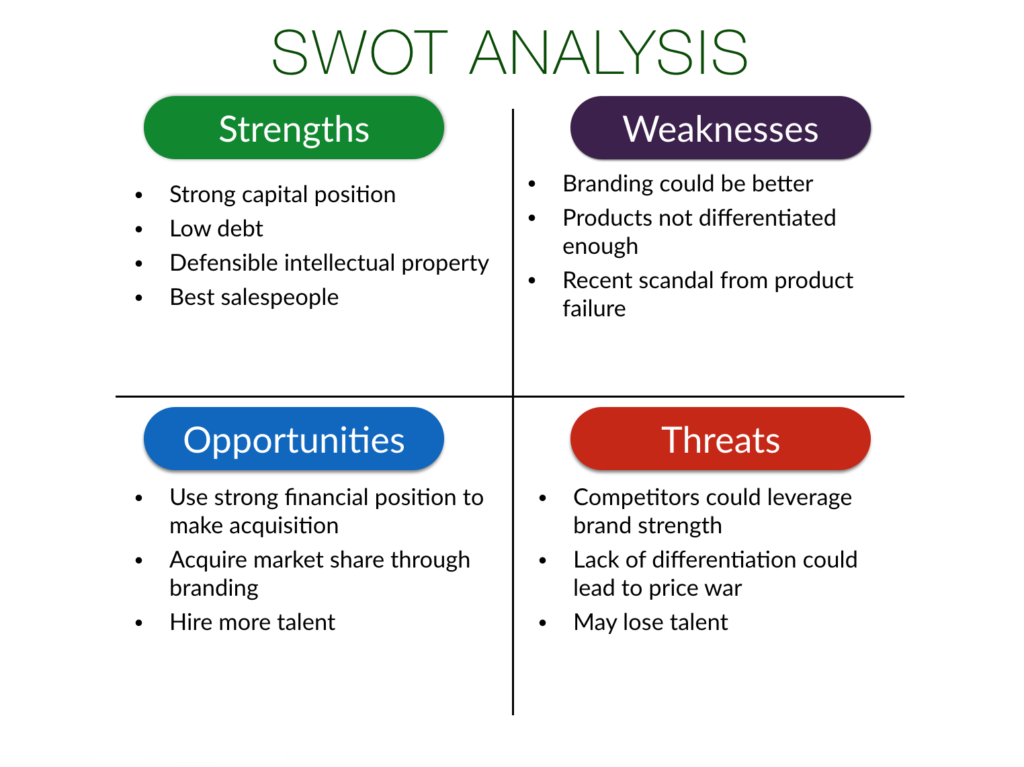
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic analysis tool used to assess accompanies present situation in the marketplace. It is another method of external analysis.
It can be used to set critical success factors and key performance indicators.
SWOT analysis helps an organization understand its environment on capabilities by using internally and externally generated information, both financial and non-financial.
With SWOT analysis and corporate appraisal on organizations, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats are ascertained.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
An organization wants to capitalize on strengths, Sure up weaknesses, invest in opportunities, and identify threats.
Strengths
An organization’s Strengths are its skills and capabilities.
- What an organization is good at.
- What resources and competencies do the organization excel at.
- what the organization does well that its competitors cannot
- A major organization success
- What is the organization’s unique selling point?
- What factor means that an organization gets that sale
Capitalizing on strengths,
Strength could be many toe opportunities. For example, suppose you have a particular strength that matches a new industry opportunity. In that case, it should be relatively easy for you to enter that industry and achieve a high market share.
Weakness
An organization’s weaknesses are what an organization is poor at.
What needs to be improved, the things that are not doing but should be where resources are in short supply and organizations major failures.
Shore up weaknesses
Weaknesses can be converted into opportunities. This can be done by identifying critical success factors and key performance indicators.
For example, if you are weak in an activity vital for a new industry opportunity, you can decide not to pursue this opportunity.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Or you can design critical success factors and key performance indicators around improvement in the area of your weakness, allowing you to enter the industry and compete successfully.
Opportunities
An organization’s opportunities are events or changes in an organization’s external environment that can be exploited, their things that are likely to go well in the future.
Invest in opportunities.
Once opportunities are identified, an organization can develop strategies to exploit these opportunities.
Threats
An organization’s threats are events that change in an organization’s external environment that must be defended against. They’re things that are likely to go bad in the future.
Identify threats
An organization can look for strategies that use strengths to overcome threats.
SWOT Analysis Summary
With SWOT analysis, always ask, What does this mean for the business? Identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats on their own is useless without analysis.
Strengths and weaknesses are internal environments that are within the control of the organization.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Opportunities and threats are external environments that are not within the organization’s control but can be impacted by the organization.
Remember, with SWOT analysis, always ask, what does this mean for the organization?
SWOT analysis is used by organizations to understand their environment and their internal capabilities better. This better understanding helps with strategic planning on improved organizational performance.
What makes SWOT analysis particularly powerful is that it helps a strategic planner uncover opportunities well placed to be exploited.
And by understanding your organization’s weaknesses, the strategic planner can manage and eliminate threats that would otherwise catch the organization’s unawares.
SWOT analysis can be used to craft strategies that help distinguish an organization from its competitors to compete successfully in a marketplace.
