David Kolb Learning Style Inventory & Kolb Experiential Learning Theory
What is Kolb Learning Style Inventory?
The Kolb Learning Style Inventory is an assessment tool developed by David Kolb. It assesses the way that you learn and how you deal with ideas and day to day situations.
We all learn in different ways, inventory conserves as a stimulus for you to interpret and reflect on the ways that you prefer to learn in specific settings.
David Kolb Learning Style Inventory
How to use Learning Style Inventory effectively.
The question is, Does one teaching style fit most to one teaching style may provide a stellar fit for some learners but find others hopelessly lost in a wealth of excess material.
Another style may fit some participants to the proverbial T, but be stretched thin on the remainder of the class.
David Kolb’s Learning Styles Inventory is based on his experiential learning model.
According to this model, learning is based on;
- Concrete experience
- Observation of and reflection on that experience,
- Formation of abstract concepts based upon the reflection and
- Testing the new concept
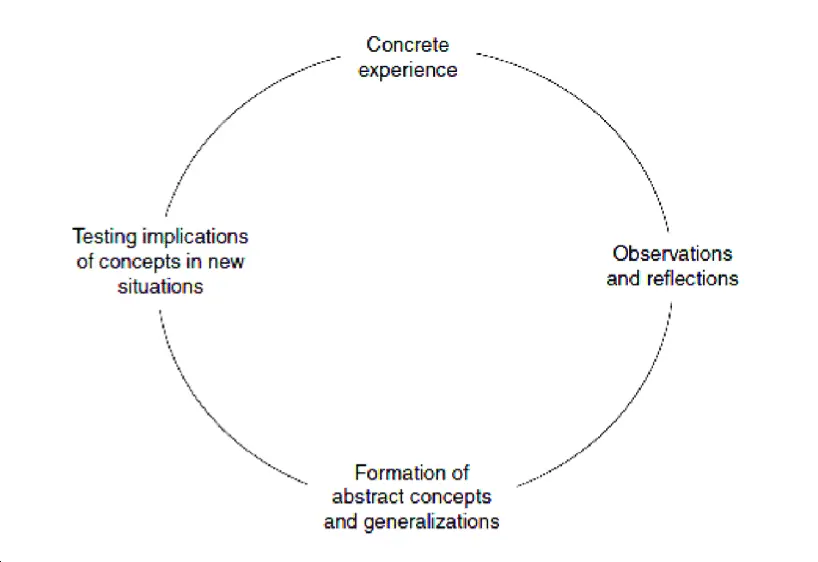
David Kolb’s Learning Style Inventory is one of several learning style models that have been developed.
Other examples include;
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator.
- Felder- Silverman’s Felder Silverman Learning style model.
- Neil Flemings and Colleen Mills VARK Guide to Learning Styles and a number of other models designed to help instructors understand how they and their students learn.
The Kolb learning style model is divided into four different styles, which derived from a four-stage learning cycle. This learning theory provides an understanding not just of individual learning but also of the four quadrants and explains the cycle of learning that can be applied to all learners
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
David Kolb presented four learning styles in his learning styles inventory;
They include; Accommodating, Assimilating, Converging, Diverging
Kolb’s intent was to develop a holistic framework with which to approach teaching and learning. Kolb used X-Yaxes as a basis for this framework.
He positioned perceiving dimensions: concrete experience, or feeling and abstract conceptualization or thinking on a vertical Axis
David Kolb placed processing dimensions: active experimentation or doing, and reflective observation or watching on a horizontal axis.
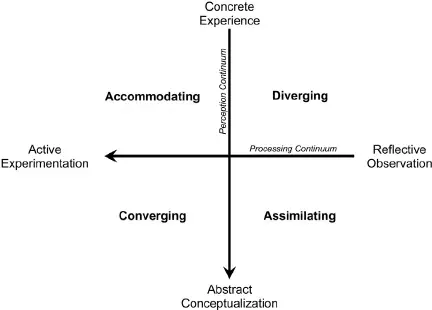
Each of the learning types falls into one of the quadrants, demonstrating a blend of a perceiving and processing dimension.
Kolb perceived his learning styles as indicators of dominant learning tendencies, not a strict method to use him defining an individual’s learning style. Ultimately, there is a subtle and complex relationship between learning and individual abilities and problem-solving skills.
Kolb also recognized that most people are not exclusively one kind of learner.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Kolb further stated that within this learning cycle, all four processes must be implemented in order for optimal learning to occur.
- Concrete Experience (CE) + Reflective Observation (RO) = Diverging Learning Style
- Reflective Observation (RO) + Abstract Conceptualization (AC) = Assimilating Learning Style
- Abstract Conceptualization (AC) + Active Experimentation (AE) = Converging Learning Style
- Active Experimentation (AE) + Concrete Experience (CE) = Accommodating Learning Style
Each mode of the learning cycle indicates one step toward the completion of a full learning experience. Learning is not linear and therefore, anyone can begin at any point in the cycle. But they would need to go through all of these stages and all of these cycles in order to really complete the learning experience.
How do you determine your learning style in the Kolb learning style?
To determine this one, you actually will need a Kolb learning style inventory it has to be completed.
There are some quick assessments that will give you a good idea, but they certainly are not as reliable.
The results of the actual inventory are very good, very reliable, and they are going to identify one of your four learning style types:
- Accommodating
- Assimilating
- Converging
- Diverging.
Accommodating Learning Style
The accommodating learner occupies the upper left quadrant of Kolb’s framework between the concrete and active axes, indicating a preference for combining feeling or intuition with doing.
Accommodators prefer to participate in controlled situations and are doers. People who can carry out plans and get involved with new projects.
According to Kolb’s Learning Skills Profile, accommodators are associated with action initiative, leadership, and relationship skills.
Accommodators are people-oriented. These are people, they are extroverts. They’re the extroverts of that Kolb learning style. Accommodators are action-oriented, their task motivated and they’re very creative in their thinking process while they take risks and they also will avoid routine routines.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
These people don’t really like routines they have feelings and intuition.
Accommodating Learning Style Example
Converging Learning Style
The converging learner is in the lower-left quadrant of Kolb’s framework between the abstract and active axes, indicating a preference for combining thinking with doing
Converging Learners excel in a technical task. Their greatest strengths are problem-solving decision making and the practical application of ideas.
Kolb’s learning skills, profile attributes, converging learners with action, goal setting technology, and quantitative skills.
Converges also prefer to work alone, but with their own ideas. They search for well-defined tasks. They learn by trial and error this type of learner an expert problem solver.
Although they generally like to work independently, they work alone.
Converging Learning Style Example
Assimilating Learning Style
The assimilating learner is in the lower right quadrant of Kolb’s framework between the reflective and abstract axes.
Assimilators prefer thinking and watching. They like to solve problems by inductive reasoning.
Assimilating learners tend toward theoretical professions and are less concerned with people than ideas.
Prefers the most logical course of action, with their strength being thinking and reflecting, and sometimes they even overact.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The logic, organization, and a strong sense of control are essential characteristics for assimilators.
They benefit most when given time to reflect on new information.
According to Kolb’s learning skills profile, assimilators are associated with quantitative theory, information analysis, and information gathering skills.
Assimilating Learning Style Example
Diverging Learning Style
The diverging learner occupies the upper right quadrant of Kolb’s framework between the reflective and concrete axes.
Diverging learners or people-oriented and tend to rely on watching and feeling or intuition. This type of learner solves problems by taking risks and his best generating alternative ideas and imaginative solutions.
Kolb’s learning skills, profile associates, diverging learners with information gathering sense, making help and relationship skills.
The diverging learner is both concrete and reflective. These learners search for the answers to why and how they learn best by observing, gathering information, and avoiding conflict whenever possible.
Diverging Learning Style Examples
Learning Style Strategies
These brief descriptions of Kolb’s four learning styles demonstrate both similar and diverse tendencies among the learning styles.
Styles that adjoin each other on Kolb’s framework may benefit from similar teaching styles.
Those in diagonally opposing quadrants require different yet supporting approaches.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Therefore, teachers and trainers should identify and understand their students learning styles in order to design programs that address the learning process as a whole.
For instance, trainers should take the learning styles inventory themselves in order to have an understanding of how their respective learning styles affect their personal teaching styles.
Learning styles inventory provides a framework to examine one’s own approach to learning situations and depending on the learning material in the situation one’s own strengths and weaknesses.
By being aware of these factors, trainers are better prepared to apply them to create effective training programs.
Varying teaching techniques
For instance, trainers should vary their teaching techniques in order to address the different learning styles.
Learning Modalities
Trainers should also consider using learning modalities that acclimate participants to learning styles other than the one each prefers becoming accustomed to.
Reduces Barriers
Using other learning styles reduces learning barriers created by the inflexibility of personal learning styles.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Compensation
There are times when trainers have to compensate for a restrictive training topic or facilities they cannot rearrange in such cases, incorporating strategies, Resource is or other aides will help learners to work in another learning style without first gaining the skills needed for that style.
Alternatives
The best strategy for these situations is to find alternatives to overcome the weaknesses. Trainers who will be working with the same group of participants over an extended period of time may include new learning style skills in their overall programs.
To do so, the trainer develops training strategies that will assist the learner in developing greater strength of skill in another learning style.
Providing even a minimal level of competence in an additional learning style helps the person learn more effectively, and they reduce the potential need for compensation in future sessions.
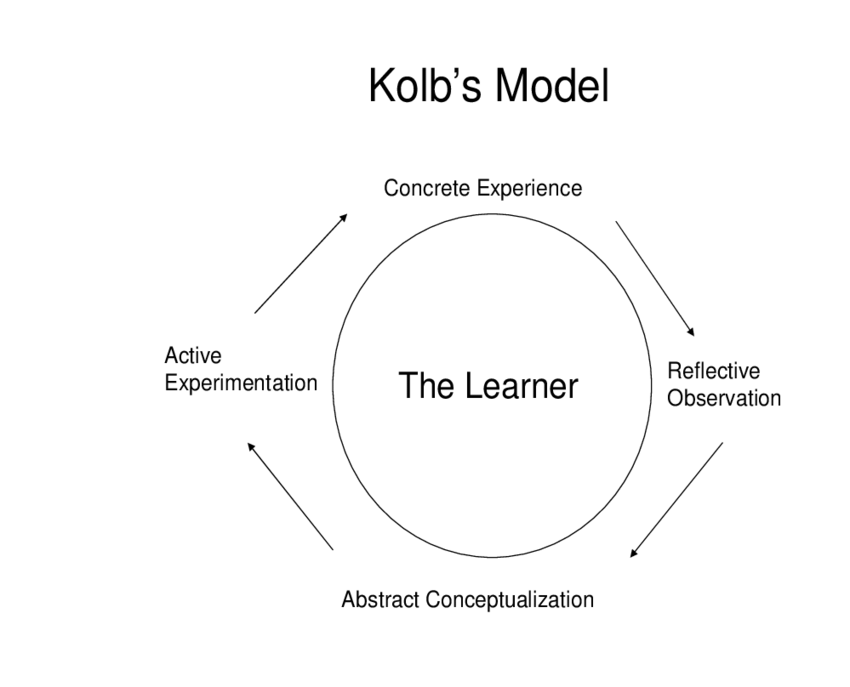
David Kolb Experiential Learning Theory Model
The Experiential Learning Cycle is the most widely recognized and use concept and experiential learning theory.
The cycle contains four stages.
- Experiencing
- Reflecting
- Thinking
- Acting
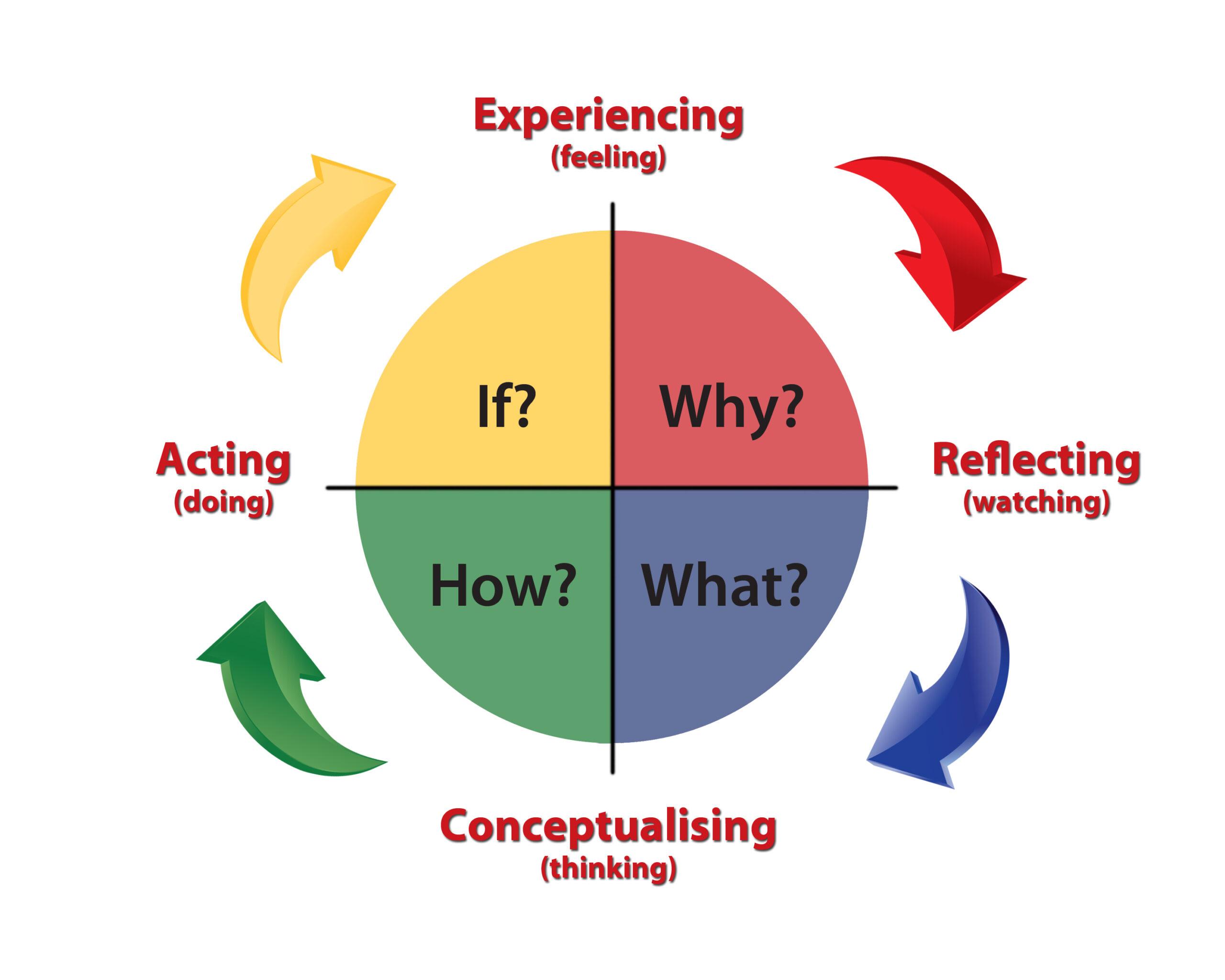
This is a simple and adaptable framework for creating educational programs that actively engage learners providing an alternative to the traditional model of information transmission
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Within this Kolb learning style, we have four learning modes, and these are ;
- Concrete experience
- Reflective observation
- Abstract conceptualization
- Active experimentation
Kolb Concrete Experience
The concrete experience mode describes people who feel more than they think. Individuals in this mode tend to be very good at relating to others, and they tend to be intuitive decision-makers.
Concrete Experience Example
Reflective Observation Learning Style
The reflective observation mode describes people who would rather watch and observe rather than be active participants.
These people like the exposure, but they don’t really want to get their hands journey.
Reflective Observation Example
Abstract Conceptualization
The abstract conceptualization mode describes people who think more than they feel these air your scientists right. These are people who have a scientific approach to problem-solving as opposed to them or an artistic approach.
Abstract Conceptualization Example
Active Experimentation Kolb
Lastly, that active experimentation mode describes individuals who take an active role in influencing others as well as a situation. These individuals appreciate practical applications rather than reflectively understanding what is happening. They want to participate, not observe.
Active Experimentation Example
Active Experimentation learning activities can include but are not limited to, hands-on laboratory experiments that the learner participates in.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Experiential Learning Cycle Model
Kolb continued his research, and he learned that learning itself is on a cycle, and he proposed that learning occurs through experience.
Within his theory of experiential learning is 8 key attributes, namely;
Learning is an endless recurring cycle/process
The Learning Cycle is an endless process of exchange between a learner’s internal world and their external environment, it is a lifelong process of taking in and putting out.
For educators, the learning cycle is about impression and expression. We impress learners with the knowledge necessary to live and work in today’s world and coach them to express what they have learned in highly skilled ways.
In traditional education, information is merely transferred from the teacher to the learner.
Paolo Freire called this the banking concept of education, where ideas were deposited into the minds of passive learners.
Experiencing is necessary for effective learning
In the learning cycle, we receive information through concrete experience, and abstract conceptualization and transform it through reflective observation and active experimentation where both receivers and creators of information.
If learning has taken place, our actions affect the next experience, and the cycle continues with ever increasing depth of understanding and skill. The cycle doesn’t just repeat it evolves.
Experiencing mode of the learning cycle is widely misunderstood. It is often equated with doing but all modes of the learning cycle our experiences.
Everyday experience is saturated with the interpretations of past generations.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
John Dewey emphasizes that to initiate reflection and learning, we need to be stuck with a problem or struck by the strangeness of something outside of our usual experience. William James called this pure experience.
When we have a concrete experience that violates the expectations of previous beliefs or behaviors, it activates reflection the next part of the cycle.
The brain is built with experiential learning
There have been a number of studies that examine the relationship between the learning cycle and brain functions.
Perhaps the most systematic is James Zull’s Research reported in his two great books, The Art of Changing the Brain and From Brain to Mind. He emphasized that knowledge resides in networks of neurons in the neocortex built by experience.
Learning from experience results in actual physical changes in the brain. You could say that educating is the art of changing the brain.
While acknowledging the greater complexity of brain functioning, Zull proposed that specific regions of the brain were involved in the modes of learning cycle.
The sensory cortex receives information from the outside world through our concrete experiences. The back integrative cortex creates meaning out of sensory information through our reflective observations.
The front integrated cortex helps us think and plan through problems with abstract conceptualization.
The motor cortex facilitates action. Action closes the learning cycle and reconnects the processing inside the brain with the world.
It generates consequences that create new experiences that begin the cycle new.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The dialectic poles of the learning cycle are what motivates leaning
What makes a learning cycle go? What motivates us to learn?
The answers to these questions lie in the dialectic poles of opposing modes of the learning cycle, concrete experience and abstract thinking, or two fundamentally different ways of understanding experience.
William James called these percepts and concepts. perception exist in the here and now. Conception points to the past or future.
James uses the analogy of a pair of scissors in the same way we need both blades to cut. We need both concrete experience and abstract thought to make sense of the world
Reflecting and acting or similarly opposing ways of transforming this understanding.
The great educator Paulo Freire stressed the importance of Praxis, the transformative dialectic between reflection and action. When either action or reflection is over, emphasized learning becomes impossible.
Hyperactivity or withdrawal into reflection both inhibit learning. Dogmatic beliefs leave us close to new experience while total immersion clouds clear thought.
The shock and awe of an intense experience can cause reconsideration of an entrenched belief. While a new idea could reshape the way, we experience things
Reflection on the consequences of action conserve to correct errors and refine future actions while acting on reflections prevents getting lost in thoughts.
Learning style are different ways of going around the learning.
Learning style is another popular concept and experiential learning theory. It emphasizes that individuals learn in different ways, and the educators can better facilitate their students that they understand their unique learning style.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Learning style is formed when one or more of the learning modes are preferred over others. The recognition of a learning style allows flexibility and education, engaging all modes of the learning cycle in a holistic and fluid manner.
Full cycle learning increases learning flexibility and development
Full cycle learning is the ability to engage all the learning style types in a holistic and fluid manner in any given situation. Many individuals feel that their learning style accurately describes how they learn most of the time.
Others tend to change their learning approach depending on what they’re learning or the situation they’re in.
Teaching around the learning cycle with dynamic matching of teaching roles
The confusion and learning style literature have resulted in the oversimplification that educators should match their teaching style to the learning style of the student.
The dynamic matching model is a more complex but more realistic model for guiding educational practice.
In addition to considering the relationship between educator and learner, one must also consider the match of learning approach with the subject matter.
Matching educator roles with learning style has been shown to be important initially to connect with learners, but most learning requires that they continue to actively move around the learning cycle to acquire increasingly complex knowledge and skills.
The Learning Cycle can be a rubric for holistic authentic assessment
The multi-dimensional teaching and learning strategies of experiential learning require equally diverse and complex assessment methods.
Assessment should be holistic. It must adequately and fairly evaluate students Integration of the learning cycle. Authentic assessment means learners should demonstrate knowledge and skills in a real-life context drawing education close to real life.
Summary of David Kolb Learning Style Inventory & Experiential Learning Cycle Theory
Last but not least, trainers should remember that Kolb’s learning style inventory is based on his experiential learning model.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The use of this model reiterates and reinforces the material being taught and encourages focus on each of the four learning styles.
The experiential learning model also provides opportunities to use a variety of teaching strategies, helping to maintain participant interest and involvement in summary.
Kolb’s learning style inventory describes for learning styles; accommodating, assimilating, converging and diverging.
These learning styles indicate dominant learning tendencies, which are not fixed rates but a manner in which the mind operates.
Additionally, most people do not exclusively learn using a single style. In order to effectively address the different learning styles of training program participants, trainers must be aware of their own learning styles and the effect of their individual learning styles on their respective teaching methods.
By using this knowledge, trainers air better able to address the training needs of their students, strategies trainers may use to design effective training programs include varying teaching techniques, compensating for not addressing a learning style or styles when necessary, and introducing skills needed for non-preferred learning styles.
Last but not least, use of Kolb’s experiential learning model will help trainers incorporate teaching techniques that are designed to maintain participant interest and involvement.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.