Limnetic Zone Definition | Limnetic Zone Ecosystems Animals & Plants
Limnetic Zone Definition
What is Limnetic Zone?
The limnetic zone is the zone of the water body closest to the surface at which light can penetrate. This is the zone in which oxygen is produced by the phytoplankton and zooplankton and is where the most life is found.
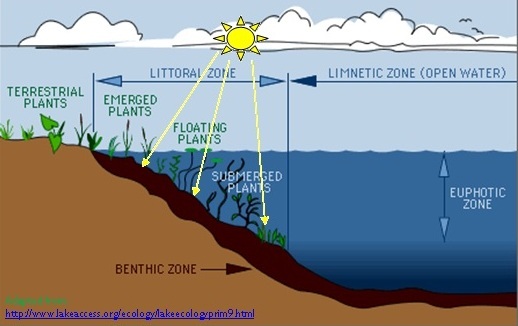
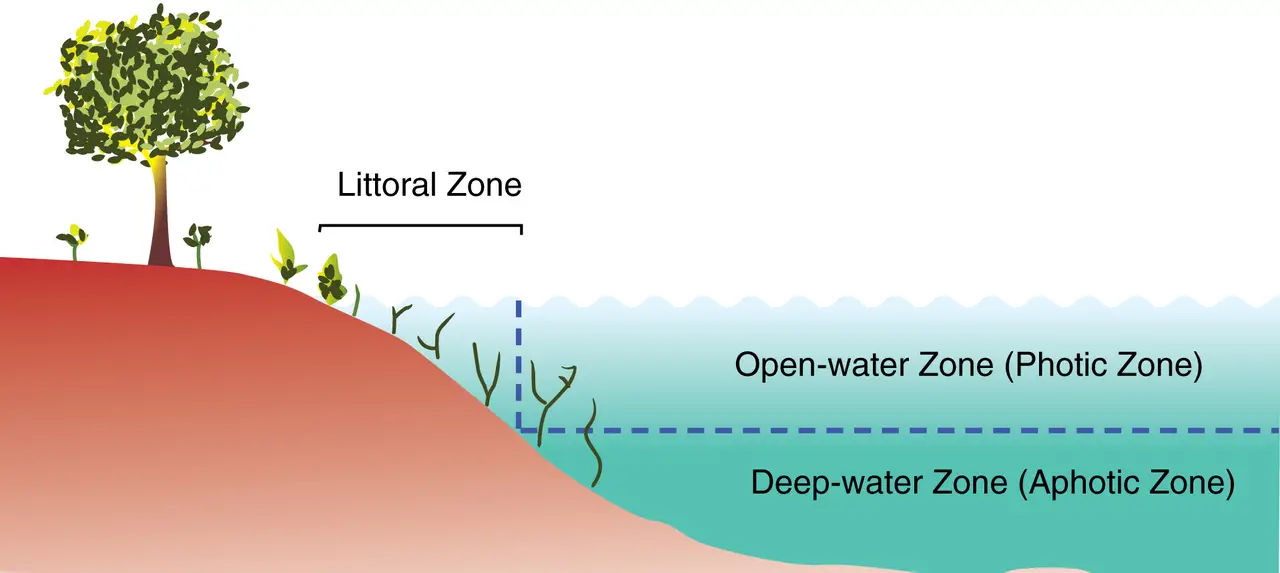
The open and well-lit area of a freestanding body of fresh water, such as a lake or pond, is known as the limnetic zone. The littoral zone, which is the shallow, near-shore region of the water body, is not included in this area. The photic zone is made up of these two zones combined.
Limnetic Zone Ecosystems
The photic zone gets its oxygen from two sources: atmospheric mixing and photosynthesis. The limnetic zone, as opposed to the profundal zone, receives enough sunlight to support photosynthesis. As a result, it is sometimes referred to as the photic zone.
Since it is the primary habitat for planktonic animals, the limnetic zone is the most photosynthetically active lake zone. Since phytoplankton populations are densest in this zone, it is the zone most heavily responsible for oxygen production in the aquatic environment.
Limnetic organisms are very complicated. Copepods, cladocerans, and rotifers are common zooplankton species found in lakes’ open water. Most limnetic populations would have one dominant copepod species, one dominant cladoceran species, and one dominant rotifer species.
Zooplanktons can move more freely in the limnetic zone than they can in the littoral zone, both vertically and horizontally. This is due to the fact that the bottom of a lake contains more sediment and substrates that create habitat niches. A limnetic zooplankton population usually consists of two to four species, each of which belongs to a different genus.
In addition to zooplankton, insects and fish are found in the limnetic region. Because of the abundance of food, many freshwater fish species remain in the limnetic zone, though these species often transition to the littoral zone as well.
Limnetic Zone Animals
The water in the limnetic zone is oxygenated at the top but very low in oxygen at the bottom. The limnetic zone is an animals’ heaven. They can find various prey, including tasty plant life, eggs, and various species of fish.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The limnetic zone is home to marine diatoms and other microscopic algae. Phytoplankton is a type of algae that uses light from the sun as a source of energy. They are found in large quantity in the limnetic zone because they are usually not consumed by larger phytoplankton.
The zone is also home to various predators, including salmon, trout, cod, and herring. It has been difficult to study this zone in more detail due to the difficult access.
Littoral And Limnetic Zone
Difference between Littoral zone and limnetic zone
The Littoral zone is the area of water near a shoreline, whereas the Limnetic zone is the area of water that extends away from the shoreline and into deeper waters.
The littoral zone contains seaweed, algae, and other plants that can be found in shallow water, while the limnetic zone contains fish like salmon or trout.
The littoral zone is the area that is near the shore and includes a variety of habitats, such as beaches, estuaries, and mangroves. In contrast, limnetic zone is where most aquatic life can be found because it has an abundance of oxygen from the water column. Animals in this zone are typically larger than those found in other zones due to their need for more food.
The major difference between the littoral zone and limnetic zones is their depth and temperature, which are different because they have different amounts of sunlight penetration.
The littoral zone has more plant life than the limnetic zone because it’s closer to land, and there are more nutrients in the water.
Limnetic Zone Depth
What is the depth of the limnetic zone?
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The limnetic zone is the uppermost layer of water in a lake or pond. It extends from the surface to a depth of about 100meters (330feet).
This zone contains animals and plants that can withstand both sunlight and oxygen deprivation.
Limnetic Zone Plants
The Limnetic zone is the upper layer of water in a lake or pond, and it extends from the surface to about 10 meters deep and contains most of the light-dependent organisms that live in lakes.
Limnetic zone plants include phytoplankton, zooplankton, and aquatic plants such as algae and mosses. These plants are mostly found near shores where there is lighter because they need sunlight to survive.
Limnetic Zone Temperature
The limnetic zone is the area of a lake that has an average temperature of 4°C to 10°C. Limnetic zones are typically found in lakes with large volumes of water and slow rates of circulation.
Limnetic zones are important because they provide habitats for fish, invertebrates, and plants.