Profundal Zone Definition | Profundal Zone Animals & Plants Ecosystem
Profundal Zone Definition
What is Profundal Zone?
The profundal zone is the area of a lake or pond that extends from the water’s surface to its deepest point. It can also be called the deep-water zone, or just “the bottom”
This region typically contains oxygen and other dissolved gases in low quantities, so it is not suitable for fish life
The Profundal zone is the deepest part of the ocean and its home to some of the most bizarre creatures on Earth. This zone is so dark that sunlight cannot penetrate through it. Creatures in this zone are adapted to living without light
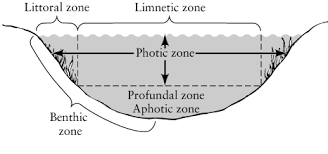
It can be found below the thermocline and epilimnion. This zone is characterized by cool temperatures and low oxygen levels. As a result, it’s an inhospitable environment for most lifeforms
It is also called the abyssal zone or hadal zone, depending on the depth. This area is home to many strange creatures that can’t be found anywhere else in the world
Profundal Zone Animals
The deep sea is the largest environment on Earth and it contains a variety of animals These include fish, squids, octopuses, crustaceans, jellyfish and other invertebrates. They are adapted to live in this zone because they have special features such as large eyes or light-producing organs that help them survive in the dark depths
Some other examples of animals that live in the Profundal zone are shrimp, crabs, worms, and amphipods
Animals that live in the Profundal Zone are typically small and have a lot of adaptations to survive.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The profundal zone is located at the bottom of lakes or oceans and can be found several tens of meters below sea level
Profundal Zone Vs Benthic Zone
The Profundal Zone is the zone of a body of water that extends from the surface to some depth where all light can no longer penetrate. In contrast, the Benthic Zone is the bottom-most layer of a body of water, extending from the seabed or shoreline down to any point where it meets with an underwater obstruction (such as rocks).
The Profundal Zone is the top layer of water in a body of water. It includes all layers from the surface to the bottom, including shallow and deep waters. The Benthic Zone is below these waters, where there are no light sources and it’s usually cold
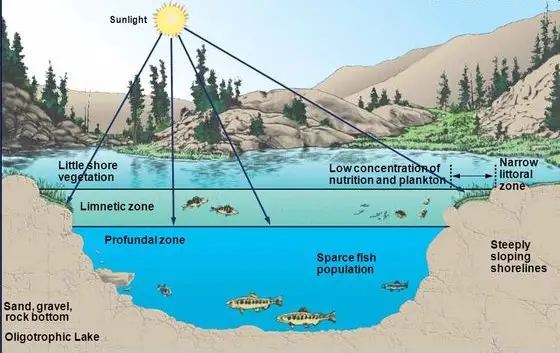
The profundal zone typically has little to no light and is not home to many organisms because it lacks oxygen. Organisms that live in this zone are typically scavengers, such as crabs and worms
Profundal Zone Plants
Are the plants in the profundal zone of a lake?
The profundal zone is the farthest depth in which no plants can grow and the only animals that may live here are fish and invertebrates. This is because the sunlight can’t reach this deep, no green plants can grow in the profundal zone.
Profundal Zone Depth
The Profundal Zone is the zone of the ocean that resides between the epipelagic and bathypelagic zones, it is from 1500-5000m below the surface. It is a zone for some of the least studied and largest creatures that inhabit the ocean, the sheer size of the zone as well as its depth making it a difficult area to study.