Mckinsey 7s Framework Example| Advantages and Disadvantages of Mckinsey 7s Model
Mckinsey 7s Framework
Most change efforts often take great effort and can be messy. It neither happens overnight nor in a vacuum, with only a select few driving the change.
Before the 1980s, this is precisely how organizations look to make the change until Thomas J. Peters, and Robert H. Waterman introduced the McKinsey 7s framework in the book In Search of Excellence, published in 1982.
McKinsey 7s Framework model shifted the focus to seven essential factors: coordinated and interdependent that included; shared values, staff, structure, strategy, systems, skills, and style.
This McKinsey 7s framework is used in a wide variety of situations where an alignment perspective is useful. It is also used to improve a company’s performance or examine the likely effects of future changes within a company or line departments and processes during a merger or acquisition process.
This McKensey’s 7s framework can help us determine how best to implement a proposed strategy. The basic premise is that seven elements need to be taken into account to ensure their alignment if a business is to be successful.
McKinsey 7s Model Hard and Soft Elements
Hard Elements
Hard elements are elements of the organization that can directly influence. They include Structure, system, strategy.
Soft Elements
Soft elements are less tangible on are more influenced by culture. They include; shared values, style, skill on staff.
McKinsey’s 7s framework visually is presented below and has several elements of the frameworks.
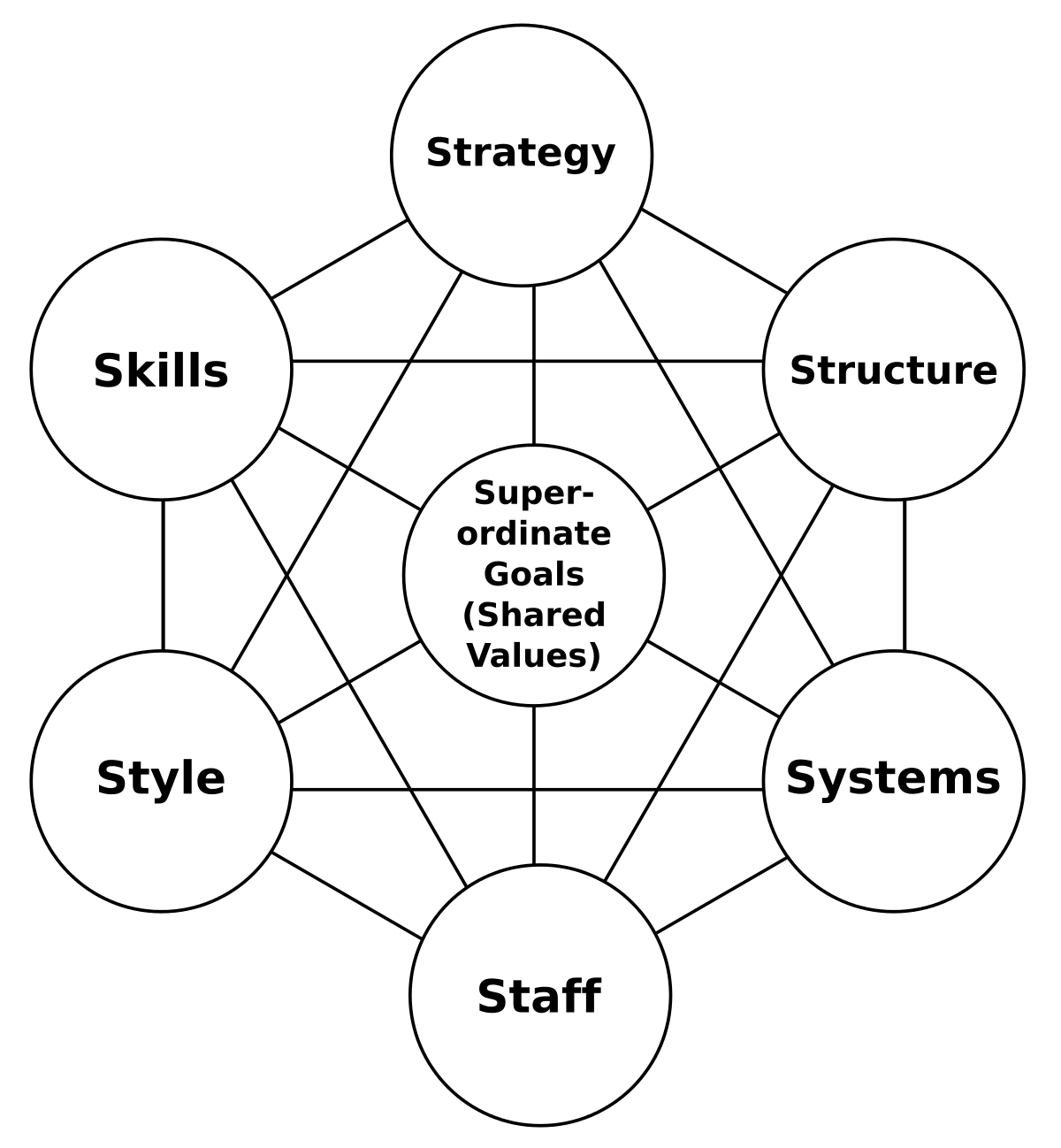
Firstly, we have strategy, structure, and systems, then supported by skills, staff, and style and all underpinned by shared values. The strategy, structure, and systems are hard elements because they are normally fixed and very procedural, and very systematic. In comparison, the shared values, the staff’s skills, and the style are referred to as the organization’s soft elements.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
McKinsey 7s Model Strategy
The strategy is the plan devised to maintain and build a competitive advantage in the competing companies’ competitive environment. Strategy details plan for the allocation of scarce firm resources over time to achieve identified goals.
Strategy deals with things like;
- How do we intend to achieve our objectives?
- How do we deal with competitive pressures?
- How are changes in customer demands dealt with?
- And how is strategy adjusted for changes in the external environment?
- What will the company do? For example, market penetration, market development, new product development, diversification.
McKinsey 7s Model Structure
The structure of the organization is the way the organization is structured. The organization and its units relate to one another: centralized, functional divisions, top-down decentralized matrix structures, or network structures. It answers the questions like ;
- Who reports to whom?
- What is the hierarchy?
- Is there a hierarchy, or is it a matrix structure?
- How do various departments coordinate their activities?
- Is decision-making and controlling?
- Is it centralized, or is it decentralized?
- Where are the lines of communication?
- How should an organization be organized, for example, functional, divisional, or network
McKinsey 7s Model System
Systems refer to the daily activities and procedures that staff members engage in to get the job done. It is about the procedures, processes, and routines used for undertaking important work. They will include the systems for financing, hiring, firing, promotion, performance appraisal systems, and information provision.
It answers the questions like;
- What are the main systems that run the organization?
- Where are the controls, and how are they monitored?
- How are they evaluated for their effectiveness?
- And what internal rules and processes does the team use to keep the organization on track?
McKinsey 7s Shared Values
Shared values refer to the company’s core values, evidenced in the corporate culture and the general work ethic. This is the interconnecting center of the McKinsey 7s model and is what’s the organization stands for, what it believes in. It is the organization’s central beliefs and attitudes.
It answers the questions like;
- What are these core values?
- What are the corporate and what is the corporate and team culture?
- How can we characterize that? How strong are these values, or would they be compromised in cases of extreme pressure?
McKinsey 7s Style
Style refers to the style of leadership adopted by the organization. The cultural style of the organization and how the key managers behave in achieving the organization’s goals. It answers the questions like;
- How participative is the leadership style?
- How effective is leadership, and do employees or team members tend to be competitive or collaborative and cooperative?
- Are there real teams functioning within the organization, or are they just nominal groups?
McKinsey 7s Framework Staff
The staff refers to the employees and their general skills and capabilities. It also captures the numbers and types of personnel within the organization. It answers the questions like;
- What positions are specializations represented within the team?
- What positions need to be filled, or what skills need to be filled?
- Are there gaps in the required competencies of the organizational team?
McKinsey 7s Model Skills
The skills refer to the actual skills and competencies of the employees working in the company. It answers the questions like;
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
- Are there any skills, gaps, how our skills monitored and assessed, particularly with changes in the external environment?
- What scale will our staff and company need? What skills does the company have? What skills are a company short on
McKinsey 7S Model Example
Let’s imagine that an elementary school in the local area is considering adopting a 1 to 1 classroom environment through the use of IPAD technology where an iPad is distributed to each student.
Shared values Example
If the school’s shared value is to foster students’ specific educational needs to produce 21st-century learners, the school would have to determine if all 7s are aligned with this vision.
Strategy Example
This particular elementary school strategy involves teachers and students collaborating in the one-to-one project, aligning with the administration’s curriculum standards.
In this way, students’ individual educational needs are met and advanced according to the shared value of creating 21st-century learners.
The organization must evaluate what skills staff and students will need to reinforce its new organizational change strategy.
Skills Example
In our example school, having staff and students participate in 1 to 1 technology training will develop their ability to function in a 21st-century learning community.
This meets the technological collaboration strategy while students develop individualized learning goals in line with the locale elementary school’s shared values.
According to educational research, professional development will be provided so that teachers will have the tools they need to facilitate student achievement.
Style Example
Looking to local elementary school management empowers teachers to create and participate in communities of practice to develop lessons and methods that support this new learning environment.
As digital natives, students are also active collaborators in these communities, which support teamwork and collaboration skills essential for 21st-century learners.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
System Example
With the 1 to 1 elementary school project, the IT department works with team leaders, administration teachers, and students to ensure the network is up to date and reliable.
In another example, purchasing managers work with administrators and teachers to determine age-appropriate equipment and software for use within the 1 to 1 program.
Structure Example
As local elementary school undergoes the implementation of the one-to-one program, keeping teachers teaching team support staff and administration accountable in a supportive but vertical environment addresses students’ specific educational needs in a style that empowers all members to focus on what’s best for pupils.
Staff Example
At local elementary schools, current teachers and staff are trained to adequately implement and support the 1 to 1 program. The new team is hired with an eye to reflect the other six areas of Mackenzie’s model.
Ideal Staff is trained and technology, interpersonal skills, and collaborative learning styles with a clear vision of what the 21st-century learner should be.
Conclusion
The local Elementary school has all elements working together to create 21st-century learners by implementing the 1 to 1 program.
Changes are desirable and inevitable in any organization, and McKensey’s 7s model provides a framework for successful change.
The organization, structure, strategy, systems, style, staff, and skills stem from its creation. It’s a shared vision.
The McKinsey 7s model gives leaders in this organization a clear and holistic guide for change that keeps all members working together and accountable to its stakeholders.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mckinsey 7s Model
Advantages of Mckinsey 7s Model
- The McKinsey 7s model is useful for achieving key corporate goals and is more effective than the traditional model that only focuses on strategy and structure.
- McKinsey’s 7s model can help bring the various departments and processes together, especially when mergers or acquisitions occur.
- The model also can facilitate the systematic application of the policies, regulations, and strategies framed by the top management.
- The model is important for effective tracking of the impact of the changes in key elements.
- McKinsey 7s model is considered a reliable theory, with many organizations adopting the model over time.
Mckinsey 7s Model Critique
- McKinsey 7s model framework emphasizes internal factors analysis of the organization’s, neglecting the external factors that substantially affect business operations.
- McKinsey’s 7s model does not provide a roadmap to follow. A big drawback with the McKinsey 7S model example is that it does not give you steps or any roadmap to follow for a change management program. It’s more of a general method to ensure your organizational elements are in balance.
- The model does not explain the concept of organizational effectiveness or performance explicitly.
- The model has been criticized for lacking enough empirical evidence to support its explanation.
- The model is considered to be more of a static kind of model.
- With the McKinsey 7s model, it isn’t easy to successfully assess the degree of fit.
- McKinsey 7s model is criticized for missing out on the intricate or finer areas in which the actual gaps in conceptualization and strategy execution may arise.