Michael Porters Five Forces Model
Michael Porter’s Five Forces was published by Michael Porter in the first article in Harvard Business Review dated April 1979. The title of the article was How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy.
Michael Porter’s Five Forces is a business strategic analysis model designed to analyze five market forces within a given industry for business competitiveness and profitability. Porter’s five forces is useful in understanding an organization’s strength in its current competitive position, and possibly the strength of a position that an organization may look to move into.
Michael Porters Five Forces Model
The five forces are frequently used to measure competition intensity, attractiveness, and profitability of an industry or market
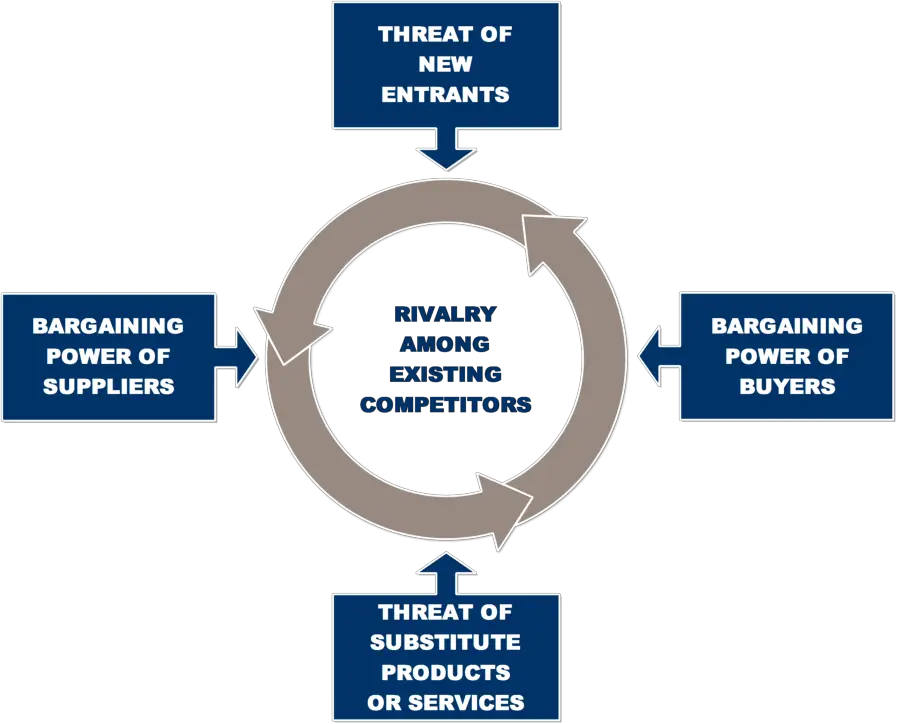
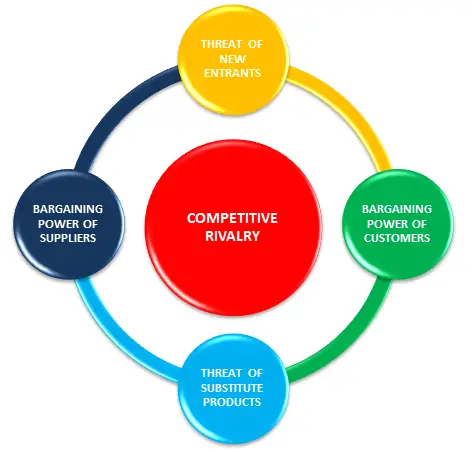
The model identifies five competitive forces, which affect the company’s competitive position. These are
- Existing competitors in the industry.
- The threat of new entrants into the industry.
- Bargaining power of the suppliers to our firm
- Bargaining power of buyers.
- The threat of substitute products or services.
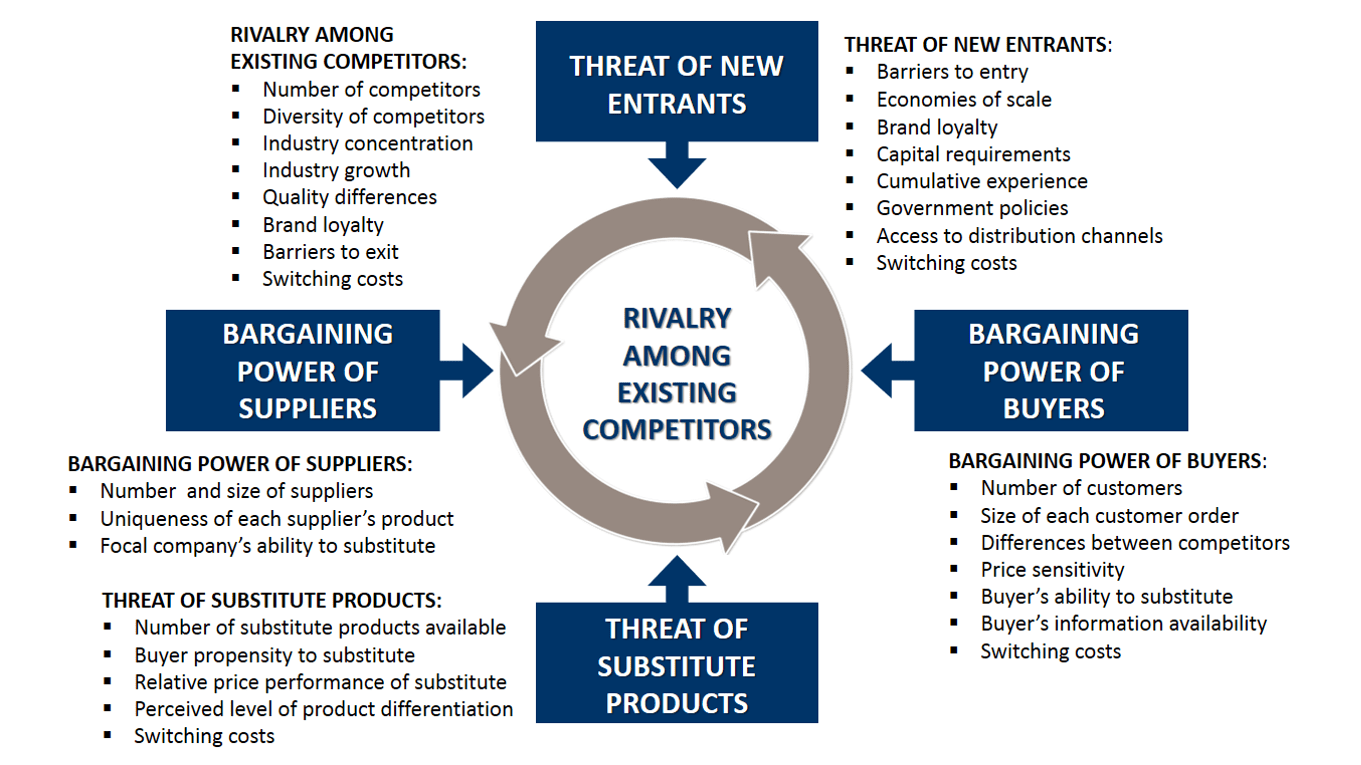
Existing Competitors in The Industry.
Rivalry amongst existing competitors takes the familiar form of jockeying for position, using tactics like price competition, product introduction, and advertising.
The intense rivalry is related to the presence of several factors. Some of the most important of these factors are;
- If competitors are numerous in the industry, the rivalry amongst these will be hard. You only have to look at cities that have a lot of fast-food restaurants.
- If the growth in an industry is slow, the firm can only grow if it gains customers from its competitors. This will intensify the rivalry.
- If the product or service lacks differentiation, rivalry intensifies. Customers can get exactly the same value from our competitors. Differentiation could be achieved with branding, as with Apple, all through offering a functionality or service that no one else includes in their products.
- If fixed costs are high, it creates a strong temptation to cut prices when demand is going down. We see this effect in price rates of cargo freight in shipping when demand for freight capacity has even a slight decline, and the price rates fall rapidly. The ship owners cannot modify the supply of capacity on they will sail as long as the running expenses are covered.
- If productive capacity can’t match demand, there will be periods of overcapacity if supply rises or demand falls; this will lead to periods of price cutting. An example is wind energy. Overcapacity conveys eyes so much that the electric power is almost given away.
- If exit barriers are high, this means that affirm suffers high cost if they stopped production in such a situation, companies in the industry will keep competing even though they may be earning low or even negative returns on investment. An example would be a firm that would have to make an environmental cleanup of the soil if they stopped production in such an industry; the rivalry would be extreme.
- If the competitors vary significantly in their strategies, origins, and personalities. An example is the health care industry; Some organizations have commercial goals. Others are non-profit organizations established to benefit humankind. They have different ideas about how to compete and continually run head-on into each other in the process.
Threat of New Entrance
The seriousness of the threat of entry depends on the barriers present and the reaction that the entrance connects pecked from existing competitors.
Some of the primary sources of barriers to entry in an industry are;
- When firms in an industry have economies of scale in fields like production, research, distribution, and marketing, then it is difficult for a new competitor to enter the industry. Examples are firms such a McDonald’s in the fast-food industry, or Amazon, with sales and distribution over the Internet. ( Five forces analysis fast food industry )
- When product differentiation exists in the industry, the existing firms have strong brand identification, and new entrance must spend heavily to overcome customer loyalties. One of the most important entry barriers may be found in the soft drinks industry, with Coca Cola and Pepsi as classic examples.
- The capital requirement in an industry creates a barrier to entry if a company requires a large, unrecoverable financial investment upfront in order to enter the industry and compete. This limits the pool of likely entrance in sectors such as mineral extraction and computer manufacturing.
- The existing companies in an industry may have cost advantages that aren’t available to potential rivals. These advantages constrain them from the effects, such as the learning curve, favorable locations, and access to raw materials. Ikea, the world’s largest furniture retailer, has strategically placed stores and warehouses they own forests, and they have great experience in listening to customers’ needs in maintaining high-quality standards.
- Access to distribution channels. The newcomer on the block must, of course, secure the distribution of its product or service. A new food product, for example, must displace others, such as Nestle products, from the supermarket shelf by a price break, promotions, intense selling efforts, or some other means.
- Government policy can limit or even prevent market entry in some industries with controls such as license requirements and limits on access to raw materials. Most countries have some sort of regulation in sectors such as trucking, liquor, retailing on fishing. Most governments also influence entry barriers through controls such as air and water, pollution standards, and safety regulations.
- Other circumstances other than those mentioned can influence the new entrants in the industry, but these are a good starting point for analyzing new entrants’ threat.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers in Relation to The Industry.
If suppliers are powerful, they can raise prices or reduce the quality of goods and services. A supply group is powerful if the following circumstances are present;
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
- Few companies dominate the group of suppliers. An example is a grain. Five companies control almost the whole world’s trade.
- A supplier has a unique position. We can’t buy the product elsewhere, or it is costly to change supplier. By choosing a specific computer software supplier, many firms place themselves in this situation.
- Our supplier poses a credible threat of integrating forward into the industry’s business. This provides a check against the industry’s ability to improve the terms on which it purchases. We see trademarks such as Gucci and Prada acquiring their own physical or online stores in the fashion industry. This gives them a powerful position against small, independent retail stores.
- The industry to which we belong is not an important customer of the supplier group, other industries, arm or important. We are in a weak position if we want product adjustments or extra service from the supplier.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
A buyer, a group, is influential in the following situations;
- Customers purchase in large volumes. An example is the government’s purchase of large quantities of office standard products such as paper. They have a powerful position in this negotiation.
- The product the customer purchase from the industry is standard products. The buyers show that they can always find alternative suppliers, may play one company against another, as they do in the trucking industry.
- If our product represents a significant fraction of the buyer’s total cost, the buyer is likely to shop for a favorable price. If it represents a small fraction of the buyer’s cost, the buyer is usually much less price sensitive.
- If our buyers earn low profits, they will always try to lower purchasing costs even if the item does not represent a large fraction of their costs.
- If our product is unimportant to the quality of the buyers, product, or services, they are price sensitive. An example might be packaging material for steel pipes. The opposite is also true when the quality of the bias products is very affected by our product. Buyers are generally less price sensitive. An industry where this situation occurs is oilfield equipment, where a malfunction can lead to large losses.
- If our industries, product, or service does not save money for the buyer, then he is price sensitive where our product or service can pay for itself many times over the buyer is rarely price sensitive. This is true in services like investment banking on public accounting, where errors in judgment can be costly and embarrassing.
- Our position is weak and our buyers strong if they can pose a credible threat of integrating backward to make the product themselves. The producers of automobiles have often used the threat of self-manufacturer as a bargaining lever.
The Threat of Substitute Products or Services.
- Threat from substitute products means that firms from other industries, completely or partially, can capture our customers.
- Another industry’s product meets the needs of our customers. We have seen this in the camera industry today. Many needs for pictures are covered by using the camera integrated with the mobile phone. There is now almost no market for cheap on middle-range cameras anymore. The camera industry today consists only of high-end cameras.
Once you have completed the industry analysis using the five competitive forces, you must develop a business strategy. This is necessary to achieve a position in the industry that is profitable.
Porter Five Forces Model Company Example
Example of The Model; Phone Industry
We will produce a game that is to be used on mobile phones as an app.
Industry
There are many in the industry. There are players on the field we don’t even know about. The rivalry is thus very intense.
New Entrance
There are almost no costs associated with developing an app. It is often a side project for students in computer science. Threats from the new entrance are high.
Supplies bargaining power
There are many programmers who we can hire to do the work. The suppliers, bargaining power is low.
Buyers bargaining power
Buyers can look for another game. Their bargaining strength is very high.
Substitutes
Of course, an app can be replaced by a game played on a computer, but it is not as mobile, so the threat from substitute products is fairly low.
According to the analysis, it is generally a tough industry. You need to develop a highly differentiated game if you want to earn money.
💥🎁 New Year & Easter Deals On Amazon !
Don't miss out on the best discounts and top-rated products available right now!
🛒 Shop Now and Save Big Today!*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Limitations of Porter Five Forces Model /Criticism of Porter’s five forces.
- The model is often accused of being a static model in an environment that is constantly evolving. Michael Porter has responded to this criticism by stating that the model can analyze how the relationship between companies, customers, competitors, suppliers, and substitutes will develop over time, you can make predictions of the future forces.
- All five forces in the model carry equal weight, and this is not true for all companies. You can argue that buyers’ customers are more important than the other aspect of the model and that suppliers may also have a special status.
- The model looks at both suppliers and customers as if they were enemies, where you have to be the strongest. However, in many cases, it can be advantageous to treat your customers and suppliers as partners and thereby achieve some common benefits, which would not be possible if you constantly fight against each other.
Summary
Finally, it must be mentioned that Porter’s Five forces provide a solid overview of the industry’s competitive situation, which we are a part of.